351Uploads
96k+Views
27k+Downloads
Sale

Simplifying Fractions 100 Worksheets with Answers Maths Mathematics KS2
100 worksheets on simplifying fractions.
Answer sheets provided.
A good time filler or homework.
Sale

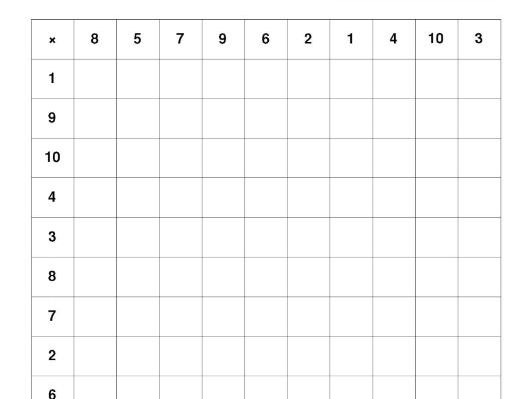
Times Tables Resource Suitable for KS2 Maths Multiplication Worksheets
100 sheets I’ve designed for times tables.
There are a variety of sheets, getting progressively more difficult.
Some are 10 by 10, some 12 by 12, some in order, some jumbled up.
The pupils have to fill in the blanks on the grid. Simple but effective.
Sale

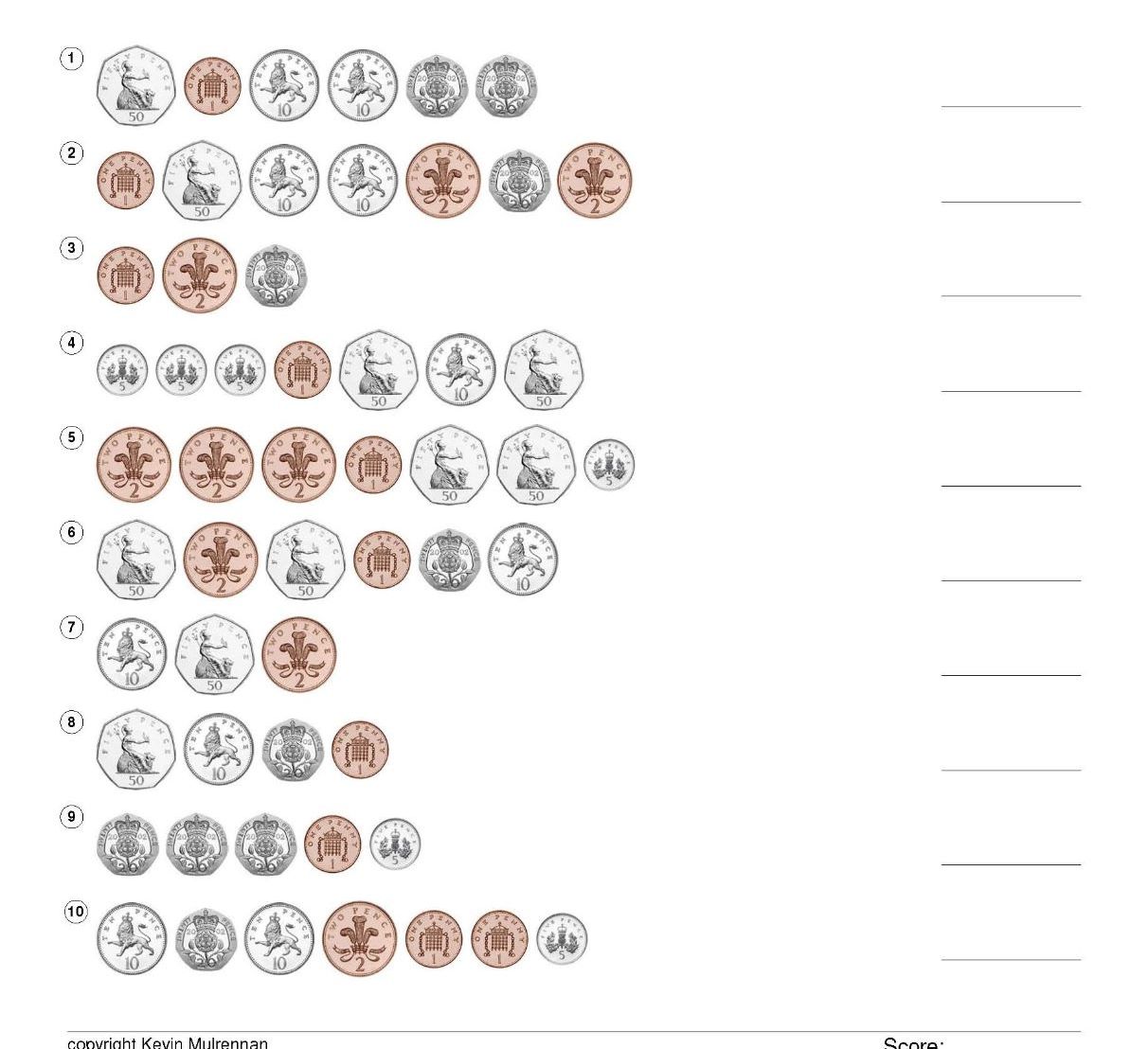
Euro Coins European Worksheets 500 Questions Mathematics Counting KS1 KS2
500 questions on counting up Euro coins.
5 worksheets with 100 questions each.
There are little pictures of the coins and the pupils have to add them up and write the answers on the sheet.
Sale

Year 5 Autumn Numeracy Mathematics Planning & Telling Time Worksheets
Reclaim your Sundays!
Year 5 Autumn planning for Mathematics.
Plus great worksheets on Telling the Time.
13 weeks worth of Maths plans.
Adapt them for your school. Cut ans paste and adapt to your needs.
Topics include
Counting, portioning and calculating
3d shapes
Securing number facts, calculating, identifying relationships
and many more
Sale

Back To School Planning Year 4 Year 5 First Week Rules Activities Powerpoints
back to school activity pack.
Ideal for year 4 and 5. Can be adapted for different years of course.
I mainly taught in these years groups, and this planning helped so much in that tricky first week,
There;s a bit of everything. Planning of course, rules, display, activities
Just packed with vital little time savers.
Some really goo VCOP stuff too.
Plenty of resources. Give it a go!
Sale

Grammar Teaching Materials Powerpoints Teaching Materials Worksheets
Gathered together all my Grammar teaching materials from Primary school.
The zip contains them all. Over 170 mb of stuff.
I’ve included a few examples in the ordinary upload so you can look.
sample:
Start by reviewing homework and making a list for the working wall.
Define each type of word: Noun, adjective, verb and adverb. Build up a sentence as we go.
Show the children a picture on the whiteboard of a horse galloping and of a lightning bolt. Children to write down 3 (LA) or 5(MA and HA) important nouns from the picture. Share. On the left of the noun, children to write an adjective to modify or describe the noun. Share. After the noun, children to write a verb and then an adverb to qualify the verb.
e.g. The black horse galloped elegantly along the beach.
Children to have 5 minutes to read and digest their new writing target. Ask any questions if necessary.
Praise the children on yesterday’s literacy work – they showed knowledge of the function of nouns, adjectives, verbs and adverbs (HA showed knowledge of the difference between common, proper and pro nouns).
Children to name a range of punctuation – I record on the board (I do not add to it at this point).
Ask volunteers to illustrate uses of the punctuation named. Look on the punctuation pyramid – have we named any L5 punctuation? This is what we should be aiming at all the time.
Children to have a variety of sentences to up level punctuation on their whiteboards.
Come back to ‘The Mysteries of Harris Burdick’. Read through all of the captions and talk about ‘reading’ the illustration. Allow children time to talk about the ‘mystery’ – what do they think happened to Harris Burdick?
Choose a picture from ‘The Mysteries…’ and list all of the questions which it provokes. What do children think of the pictures? Do the captions answer any of the questions?
Talk about the settings in the pictures – often they are recognisable, familiar settings where things are not as they seem. Explain that we would call this ‘Stories in a familiar setting’.
Model the task.
Sale

Short Term Literacy Lesson Plans Year 5 Autumn Spring Summer Terms
Some great short but punchy Literacy lesson plans.
Spread throughout the terms.
Example :
Synonyms to describe the soldier WALT: explore the main ideas of a text
WILF:
I know what the important points in a text are.
I can explain my ideas about a character.
I can find relevant information in a text.
Recap on the story. Was it fair for the soldier to kill the witch? What type of characters are the soldier and witch? Explain your ideas. Shared read an alternative version of the tinderbox. Discuss what the main points of the text are. Children to highlight what they think are important points and explain why they think this. CT to introduce tasks and explain their roles. Task: Children to work in mixed ability groups with each given a role. 1. Draw an image of a main character. 2. Record the thoughts and feelings of the character using information from the text. 3. Identify the main points of the text so far. 4. Summarise the key points of the story. Read through to page 10. What do you think might happen next? How will the soldier spend his money?
Group 1
CT to read the text with the children and discuss the key information and supplementary information. CT to check children’s understanding of the text. Task: Children to debate whether the soldier committed murder or not.
Punctuation- recap over .,!?
WALT: create dialogue between characters
WILF:
Correct use of speech punctuation
Use of adverbial phrases to extend sentences
Ability to use tone, gestures and expression to convey a characters mood.
Read the tinderbox to the page when the villagers are discussing the soldier’s new money and desire to meet the princess. Highlight the speech punctuation and discuss what the rules for speech are. CT to model examples.
Task:
Children in pairs to create a short dialogue that they can act out for the class. Children must use references to the text and expression, gestures and tone to convey the characters viewpoint. Read the line ‘I really want to see her’ – why is this in italics? What do you think the soldier will do to see the princess? Group 4
CT to support the children to use correct speech punctuation and adverbials to extend ideas.
Sale

Back to School Holes Louis Sacher Teaching Plans 5 Weeks Literacy Year 6
Great planning for Louis Sacher’s intriguing book Holes.
5 week’s short plans.
Plus great stuff on getting pupils to construct aruments. Two terrific pdfs.
Sample planning :
Spelling rules. Modifying e.
Cope … coping. In pairs write short speech for debate. Shared write persuasive language list. What connectives could be used to link ideas? What about repetition? WALT: organize views in a debate about homework. Debate “Should primary children have homework? All pairs to speak. Comment and question speakers. LA: TB to list points and useful language.
HA: to lead arguments
Add title paragraphs in example argument about Dogs in Parks. Review plan. Recap form. Read introduction through. Suggest strong openers for sentences and useful connective phrases from chart. Indiv write points for homework in Primary Schools. Paragraph – consider openings. WALT: write a balanced argument in a formal style.
Mr Pratt
Synonym Circus Recap plan and bullet points. Consider possible connectives to link to opposite view. (e.g. nevertheless) • All write points against - anticipating possible objections
homework to balance argument. Use paragraphs and strong openers.
Find passive voice in examples. Read example formal discussion regarding homework. Identify language. Useful terms. WALT: Write a formal letter of complaint. All children write complaining letter about a visit to a restaurant. LA: provide opening. Vocab list for feelings and connectives.
Example balanced arguments.
• the expression, sequence and linking of points
• the provision of persuasive examples, illustrations and evidence
• pre-empting or answering potential objections
• appealing to the known views and feelings of the audience;
T16 identify the features of balanced written arguments which:
• summarise different sides of an argument
• clarify the strengths and weaknesses of different positions
• signal personal opinion clearly;
T18 construct effective arguments:
• developing a point logically and effectively
• supporting and illustrating points persuasively
• anticipating possible objections
• harnessing the known views, interests and feelings of the audience
• tailoring the writing to formal presentation where appropriate;
T19 write a balanced report of a controversial issue:
• summarising fairly the competing views
• analysing strengths and weaknesses of different positions.
Sale

Year 5 Literacy and Maths Planning
Gathered together my lessons for year 5 Maths and English for a particular year. There’s about a year’s worth in there.
Plenty of great ideas. the zip has the lot. the general download a few to have a look at.
Sample planning :
Start by showing the word ‘Instructions’ – TTYP what does this mean?
Come back together and establish that instructions are a set of commands given to help someone do or create something.
Show the children a recipe and the instructions as to how to play Sevens using cards. Look at the instructions. What do children notice about how these are laid out? They are given in an order.
They are bullet-pointed.
Each sentence is fairly short.
There are many ‘bossy’ verbs: ‘place’, ‘play’, ‘turn’ etc. Explain that we call these ‘imperative’ verbs – an imperative is a command. Discuss why it is helpful to have ‘bossy’ verbs and short clear sentences.
There is a title which tells you what is to be achieved.
Numbers or time connectives used e.g. 1, 2, 3 or later, next - are used to show chronological order.
Create a features list on the working wall by sticking post it notes onto a piece of sugar paper –these can be used throughout the unit as a game to start the lesson.
Divide the class into three teams. Deal out seven cards to each team and the teacher! Play a little of the game of sevens, following the instructions. Demonstrate how we can follow the instructions to play.
Return to features of instructions displayed on working wall.
What can you remember about these? Children turn to a partner and tell them 3 different features. Report back & discuss.
Show children the instructions checklist (working wall). Have we mentioned all of these features?
Ask children to think of a new idea for a card game. Use a talking partner & brainstorm a game idea on whiteboards.
Gather everyone’s ideas/discuss the concepts. Pick one idea.
Decide how many players we will need & how to play it. Allow children time with talking partners to practice playing the game. Ask some children to demonstrate.
How will we write the instructions? What comes first? (Title, subheading.) What is our first instruction? Repeat for a few more sentences.
Sale

Poetry Imagery Planning Year 6 English Literature Imagery and Personification
Great planning for year 6.
Two weeks worth.
Nice powerpoints.
Sample :
Introduce the new unit and writing outcome.
Read the poem ‘Fog’ by Carl Sandberg together. Write ‘personification’ on the board and discuss what this means.
TTYP – what might it mean?
Agree on a definition for the working wall: Giving human traits to non-human or abstract things. Or making a non-human thing do things that only a human can do. Explain the phrase ‘inanimate object’.
Give out copies of ‘Two Sunflowers Move in a Yellow Room’ by William Blake. Discuss how the sunflowers are given human characteristics – they talk, they feel tired, they want a room with a view!
Return to the poem Fog. In this, it is almost as if Fog is alive – either human or possibly feline (cat-like).
Look again at ‘Two Sunflowers Move in a Yellow Room. ’Underline the words ‘topaz tortoises’.
Ask children what these last lines mean?
Discuss whether it matters if we are not sure of the exact meaning of all the words in a poem. Why might it not matter? Because it is the sound and the rhythm of the words which is as important as their meaning in a poem.
Look up topaz to find its meaning. Does this help us understand what the last two lines mean?
Sale

Year 4 Area and Perimeter Maths Lesson Plan Squares and Rectangles
Nice lesson.
Possible cross curricular links. Outside area planning.
Learning Objectives. Ma 1 Organising and explaining
Ma 3 Calculate perimeter/area of squares and rectangles.
• To explain methods and reasoning
• To solve mathematical problems, recognise and explain patterns and relationships.
• Calculate perimeters and areas of rectangles.
• Find the largest area that can be made with a rectangle that has a perimeter of 26 metres.
Success criteria.
• To be able to work out the area of a rectangle or square.
• To make different rectangles that all have the same perimeter.
• To recognise the largest area.
• To compare the relationship between the length of the sides and the area of the rectangle.
• To explain reasoning.
Mental/Oral. 10 mins. LSA to support LA children.
The answer is 16. What is the question?
Using the yes/no cards hold up the correct side in response to the question.
15 + 1, 10 + 4, 18 – 2, double 2 ……. (12 questions.)
Can we think of any more to add to the list?
Discuss any misconceptions as they arise, also the quick ways to add numbers mentally. Emphasis on bonds and doubles or near doubles.
With a partner, using InWB find as many questions as possible for the statement.
The answer is 24. What could the question be?
Vocabulary.
add
subtract
multiply
divide
double
near double
half
equals
Resources :-
Yes/No cards.
InWBs and pens.
Nice worksheets and powerpoint to do an investigation on the area and perimeter of squares and rectangles.
Possible cross curricular links. Outside area planning.
Learning Objectives. Ma 1 Organising and explaining
Ma 3 Calculate perimeter/area of squares and rectangles.
• To explain methods and reasoning
• To solve mathematical problems, recognise and explain patterns and relationships.
• Calculate perimeters and areas of rectangles.
• Find the largest area that can be made with a rectangle that has a perimeter of 26 metres.
Success criteria.
• To be able to work out the area of a rectangle or square.
• To make different rectangles that all have the same perimeter.
• To recognise the largest area.
• To compare the relationship between the length of the sides and the area of the rectangle.
• To explain reasoning.
Mental/Oral. 10 mins. LSA to support LA children.
The answer is 16. What is the question?
Using the yes/no cards hold up the correct side in response to the question.
15 + 1, 10 + 4, 18 – 2, double 2 ……. (12 questions.)
Can we think of any more to add to the list?
Discuss any misconceptions as they arise, also the quick ways to add numbers mentally. Emphasis on bonds and doubles or near doubles.
With a partner, using InWB find as many questions as possible for the statement.
The answer is 24. What could the question be?
Vocabulary.
add
subtract
multiply
divide
double
near double
half
equals
Resources :-
Yes/No cards.
InWBs and pens.
Sale

Music Planning Beethoven Greig Mozart Tchaikovsky Composer
Planning from my time in Primary Schools. PRUNING NEEDED!
Lots of music info.
Lots of great composers.
Beethoven
Greig
Mozart
Tchaikovsky
Sample :
TOPIC: Listening and Understanding Music KS1LUDWIG VAN BEETHOVENRESOURCES: dvd copy of Disney’s Fantasia; Beethoven/Pastoral sheet; pictures of orchestral instrumentsLESSON ONEWatch the Pastoral Symphony excerpt, and explain that this very old film uses music that is even older. The artists listened to the story in the music and created their story to fit it. Having watched the excerpt, ask the children what they noticed about how the music and the cartoon went together. Think about the peaceful music for the peaceful scenes; the angry music for the storm; the way the winged horses alight in time to the music etc.Watch a second time, pausing as appropriate to highlight the interaction of music and cartoon. Start to spot instruments.LESSON TWOListen to the Fantasia version of the Pastoral without the cartoon. Invite the children to recognise instruments. Show them pictures of the instruments as they name them, discussing how they are played, how their sounds differ from each other, and why they suit the different aspects of the music. Discuss the differing roles within an orchestra and look at the layout of the orchestra. Invite the children to draw a picture of their favourite instrument and explain why it is their favourite.LESSON THREEWatch the Fantasia excerpt again and remind the children that this story is the artists’ idea of the musical story. Explain that the artists used mythological characters because these were very popular in paintings at the time the music was composed (you could show them some). Invite the children to listen to the music and write their own story, or create their own picture either using the mythological characters or their own ideas.LESSON FOUR Explain that the class is going to listen to the story of the man who composed the Pastoral Symphony, and then write about him and his famous piece of music. Provide the children with paper to make notes should they wish, and the sheets to write up their findings when they are ready.
Sale

Back to School Literacy Year 6 Stories by significant authors J K Rowling
Lots of great planning for an exciting unit.
Nice powerpoints.
Sample :
Share the learning outcome for the unit with the children; share the concept of the working wall. What is narrative? Fact or fiction? Ascertain that this unit is about fiction/narrative/stories. We have three weeks to achieve our learning outcome.
Ask children what they know about JK Rowling. Who is she? What is her job? (use correct terminology- she is an ‘author) Where is she from? (Born in Gloucestershire) Can children name any of her books? (Harry Potter series plus several supplements)
Etc.
Activity One
Come back together, show children a picture of JK Rowling – does this help?
Children to move to next group’s poster and add any more info that they can now think of. Is there anything they agree/disagree with?
Lead into a class discussion on this famous children’s author:
Has anybody read any of her books?
What are her stories about? What genre do you think her stories are written in? (Clarify what we mean by ‘genre’ if needed). What is the purpose of narrative writing? (Display ‘to entertain and enthrall’ on the working wall).
Read first tale from ‘Tales of the Beadle Bard’ – The Wizard and the Hopping Pot. Discuss what is distinctive about this story (what does it remind you of?)
Sale

11 Plus Letter Patterns Volume One Logic Puzzles
100 sheets with answers.
The sort of thing that’s good for eleven plus prep.
Good for logical thinking.11+ Grammar School
Letter Pattern Questions
What do you call a rooster with a bad sunburn? A fried chicken.
Find the next two letters in the pattern for each set
of letters.
Use the alphabet grid if stuck.
KGOKS_ _ OW (- 4 + 8)
QOMKI_ _ GE (- 2)
KGPLU_ _ QZ (- 4 + 9)
FHJLN_ _ PR (+ 2)
HJLNP_ _ RT (+ 2)
GFHGI_ _ HJ (- 1 + 2)
VSPMJ_ _ GD (- 3)
SXQVO_ _ TM (+ 5 - 7)
ZXVTR_ _ PN (- 2)
FILOR_ _ UX (+ 3
Sale

Area Perimeter maths Net Cubes Compound Shapes Year 5
Work out the area an perimeter of cubes etc.
You can print out shapes and give to pupils.
Learning Objectives. Ma 1 Organising and explaining
Ma 3 Calculate perimeter/area of squares and rectangles.
· To explain methods and reasoning
· To solve mathematical problems, recognise and explain patterns and relationships.
· Calculate perimeters and areas of rectangles.
· Find the largest area that can be made with a rectangle that has a perimeter of 26 metres.
Success criteria.
· To be able to work out the area of a rectangle or square.
· To make different rectangles that all have the same perimeter.
· To recognise the largest area.
· To compare the relationship between the length of the sides and the area of the rectangle.
· To explain reasoning.
Model the way to answer the question referring to work of a few weeks ago on perimeters. How many different sized pig pens can be made using only 12 fencing panels?
Discuss how the children think they could solve this problem.
The Problem.
We want to make a school garden and grow vegetables. At night time the rabbits and deer will come and eat them. To stop them we need to put a fence around the area. However we can only afford to buy 26, one metre long panels.
Find the largest area we can fence off to make a rectangular vegetable patch?
Remember it can only have a perimeter of 26 metres.
Vocabulary.
add
subtract
multiply
dividedouble
half
equals
rectangle
square
area
perimeter
cm2
Resources:-
multi-link. L/A
rulers.
Squared paper.
Home work:- if applicable.
Assessment. Children exceeding the objectives.
Sale

Year 1 Maths English Planning
Planning for English and Maths. 56 files.
sample:
Text:
This is the bear and the scary night
Genres covered in this unit:
Narrative SPAG focus:
Monday: spelling patterns
Tuesday: use and to join clauses
Wednesday: high frequency words
Thursday: high frequency words
Friday: time connectives
Key teaching input/texts/questions/
clips etc Steps to Success
Read the story This is the Bear and the scary night
Discuss character, setting, key events etc…
Discuss what happened in the beginning, middle and end of the story. Explain to the children that this week they are going to write their own story similar to the bear and the scary night.
Ask children to describe their character to their partner (can be their favourite toy or the teddy they bought into school on Friday).
Ask children to share their ideas about their story.
What is the setting?
What are the characters doing?
What is the problem?
How are the characters feeling?
How does your story end?
Mild: describe your main character
Spicy: share your ideas with your partner
Hot: listen attentively to your partner
Extra Hot: Act out key events from your story
LA Activities MA Activities HA Activities
Read to Write
Mrs Preston Phonics
Mrs Simpson Talk for writing and act out their story
Photos for books
Resources: The bear and the scary night book, cards with questions
Give 3 minutes for children to recap their story.
Who is their main character?
What happens at the beginning, middle and end of the story?
Model how to put key ideas onto their plan.
Steps to Success
Mild: recap your story with your partner
Spicy: Identify the beginning, middle and end of your story
Hot: Write key ideas onto your story plan for the beginning, middle and end.
Extra Hot: Check your partner’s plan is sequenced correctly
Bundle Sale

Bundle Coins plus Across Down Subtraction and Addition
A bundle.
Coins worksheets plus ones on acoss down puzzles (subtraction and addition)
Teaching Resources 100 worksheets Coins KS1 Teachers Counting KS1 KS2
2
KS2 Mathematical Puzzles Across Down Subtraction
2
Maths Puzzles Across Down Addition 100 Puzzles Plus Answers

Latin Word Search Freebie plus answers Cambridge Latin Course
A freebie.
A Latin word search.
If you like this one, I have 500 for sale in my shop.

Maths Puzzle Across Down Addition and Subtraction Puzzle Plus Answers
Great for reinforcing maths.
Across-Downs is a fun activity that reinforces addition and subtraction skills.
The object of the exercise set is to find the answer for each row and column, then use those answers to calculate the final answer in the lower right-hand corner of the puzzle.
This tests addition and subtraction.
If you like this freebie, please visit my shop which has loads of puzzles for sale. Buy the bundles for best value.

Freebie 2 French Wordsearches KS1 KS2 Perfect for Friday Afternoons With Answers
2 French wordseaches with answers.
Each one has 20 basic words to find.
Perfect for rainy Friday afternoons, homeworks etc.
If you like these, please visit my shop where you can purchase 500 of these at a very reasonable price.