

This lesson describes how the structures of the xylem vessels, sieve tube elements and companion cells relates to their functions. Both the engaging and detailed PowerPoint and accompanying resources have been designed to cover point 3.1.3 (b) [i] of the OCR A-level Biology A specification.
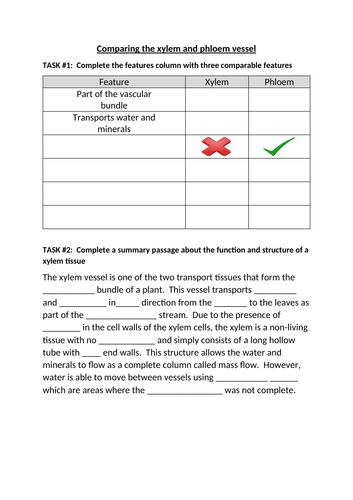
The lessons begins by challenging the students to identify the substances that a plant needs for the cellular reactions, where they are absorbed and where these reactions occur in a plant. The aim of this task is to get the students to recognise that water and mineral ions are absorbed in the roots and needed in the leaves whilst the products of photosynthesis are in the leaves and need to be used all over the plant. Students will be reminded that the xylem and phloem are part of the vascular system responsible for transporting these substances and then the rest of the lesson focuses on linking structure to function. A range of tasks which include discussion points, exam-style questions and quick quiz rounds are used to describe how lignification results in the xylem as a hollow tube of xylem cells to allow water to move as a complete column. They will also learn that the narrow diameter of this vessel allows capillary action to move water molecules up the sides of the vessel. The same process is used to enable students to understand how the structures of the companion cells allows assimilates to be loaded before being moved to the sieve tube elements through the plasmodesmata.
It is estimated that it will take in excess of 2 hours of A-level teaching time to cover the detail which has been written into this lesson
Get this resource as part of a bundle and save up to 33%
A bundle is a package of resources grouped together to teach a particular topic, or a series of lessons, in one place.
Something went wrong, please try again later.
This resource hasn't been reviewed yet
To ensure quality for our reviews, only customers who have downloaded this resource can review it
Report this resourceto let us know if it violates our terms and conditions.
Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.