DC Motor GCSE AQA Physics 9-1 PowerPoint
For GCSE AQA Physics (and as an introduction to AQA A-level Physics)
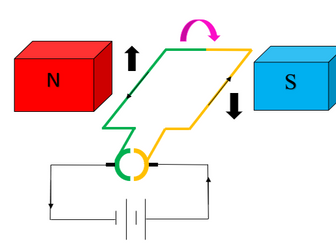
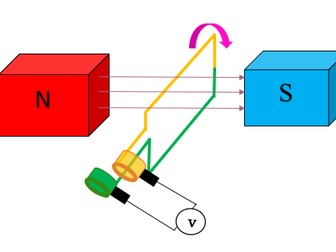
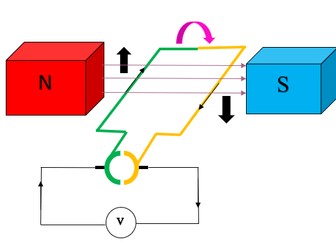
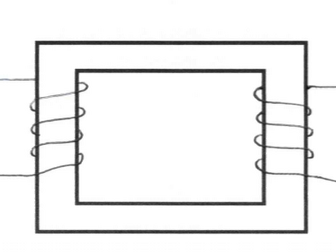
Parts of DC motor
Explains why forces occur on the coil
Step by step explanation of the forces occurring on the coil at each position
Explains purpose of split ring commutator
Key points to learn for DC motor