BTEC Applied Science Unit 1 - Biology B1, B2, B3
This is a complete scheme of work for the BTEC applied science Unit 1- Biology B1, B2, B3 section. All information has used the ‘additional guidance’ published by BTEC in addition to the specification.
Lessons:
1-2 eukaryotic celsls
4-5 prokaryotic cells
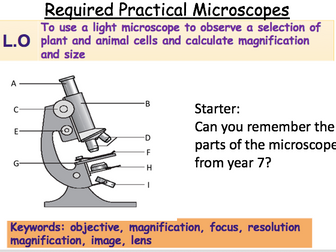
6- using a microscope (adapted a powerpoint beloning to author - ‘Bigarthur’ resources) * (see below)
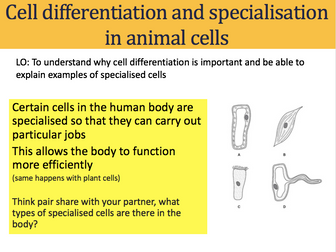
7-8 cell specialisation (not included due to copywrite)
10- squamous tissues
11- collumnar epithelial cells
12- muscular tissue
12- fast/slow twitch fibres
14-15- nervous tissue
16- synapses
Included are:
Lesson powerpoints with a variety of activities to encourage student engagement, Worksheets and exam practice - (including lots of opportunities for extended writing and exam technique looking at the examiners report), a lesson overveiw/ order of teaching and a mini assessment at the end. Also includes starters for every lesson which either build on GCSE knowledge revision or use spaced learning to improve student’s recall of infomation previously covered.
Please go to my store to purchase the homeworks as these are not included in this scheme.
I have also not included the cell specialisation lesson as I have used another teachers resource for this lesson.
credit to ‘bigarthur’ who’s resource i have adapted for the microscopy lesson. To save you time on finding this i have included it in my resources but not added it into the cost of this resource.