Electrochemistry: Understanding Galvanic Cells
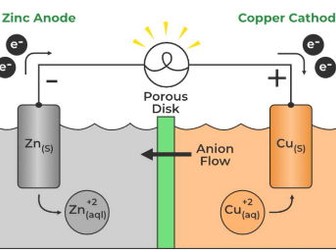
Galvanic cells convert chemical energy into electrical energy through spontaneous redox reactions, forming the basis of battery technology.
These cells consist of an anode, where oxidation occurs, and a cathode, where reduction occurs, connected by an electrolyte and an external circuit.
The flow of electrons from the anode to the cathode generates an electrical current, driven by the difference in electrical potential between the two electrodes.