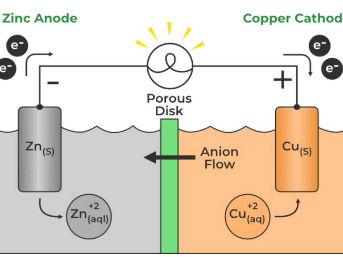

Galvanic cells convert chemical energy into electrical energy through spontaneous redox reactions, forming the basis of battery technology.
These cells consist of an anode, where oxidation occurs, and a cathode, where reduction occurs, connected by an electrolyte and an external circuit.
The flow of electrons from the anode to the cathode generates an electrical current, driven by the difference in electrical potential between the two electrodes.
Something went wrong, please try again later.
This resource hasn't been reviewed yet
To ensure quality for our reviews, only customers who have purchased this resource can review it
Report this resourceto let us know if it violates our terms and conditions.
Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.