B7 Ecology - L1 Communities and Food Chains
Lesson 1: Communities and Food Chains
Perfect for: GCSE (KS4) | AQA Combined Science Trilogy
Topic: B7 Ecology — Lesson 1: Communities, Food Chains & Food Webs (All Abilities)
Engaging recall-based Do Now to reactivate prior knowledge (osmosis, transpiration, communicable disease, limiting factors, blood glucose regulation)
Lesson 1: Communities and Food Chains
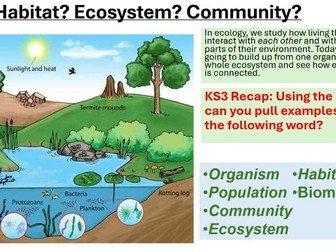
Clear breakdown of ecosystems, communities, populations, habitats & biomes using visuals and modelling
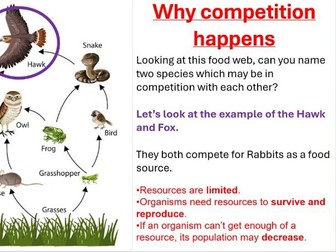
Introduction to energy flow, photosynthesis as the energy source, producers, consumers and trophic levels
Misconception tackling (e.g. arrows in food chains do not mean “is eaten by” but show energy transfer)
Explains energy losses across trophic levels with linked 3-mark exam question + mark scheme
Includes decomposers + introduction to niches with real-life examples
Short retrieval checks (MWB) throughout for assessment for learning
Plenary exam questions reinforcing key vocabulary and command words
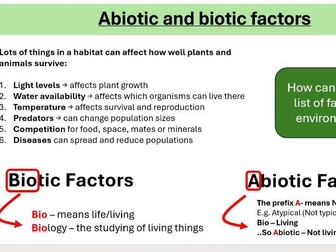
Sets up further lessons on interdependence, abiotic/biotic factors, and ecosystem regulation
What’s Included
Fully editable PowerPoint lesson
Knowledge checks + interactive MWB tasks
Exam practice with mark schemes
Real-world case context (Yellowstone wolves)
Tier-accessible scaffolding + challenge stretch
Literacy + key terminology emphasis
Mapped to AQA Combined Science Trilogy (8464):
B7.1 Ecology overview
B7.2 Levels of organisation
B7.3 Food chains & food webs