

A KS4 lesson aimed at a mixed ability/Middle ability (MAP) pupils. Students learn what enzymes are, how they work, and their role in digestion. The lesson introduces enzymes as biological catalysts, explains the lock and key model, and explores the roles of amylase, protease, lipase, and bile in the digestive system.
From AQA GCSE Combined Science / Biology (Digestive Enzymes):
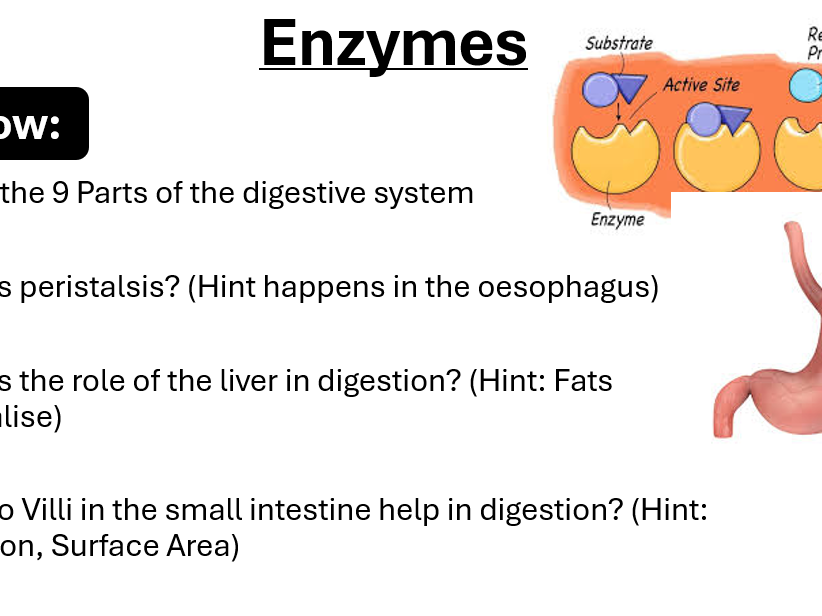
Enzymes catalyse specific reactions in living organisms due to the shape of their active site.
Use of the lock and key theory as a simplified model to explain enzyme action.
Recall of enzyme production sites and functions:
Amylase (carbohydrase) breaks down starch into sugars.
Proteases break down proteins into amino acids.
Lipases break down lipids into glycerol and fatty acids.
Understanding of word equations for enzyme reactions (no symbols required).
Digestive enzymes convert food into small soluble molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream.
Bile functions: neutralises stomach acid and emulsifies fats to increase surface area for lipase.
Something went wrong, please try again later.
This resource hasn't been reviewed yet
To ensure quality for our reviews, only customers who have purchased this resource can review it
Report this resourceto let us know if it violates our terms and conditions.
Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.