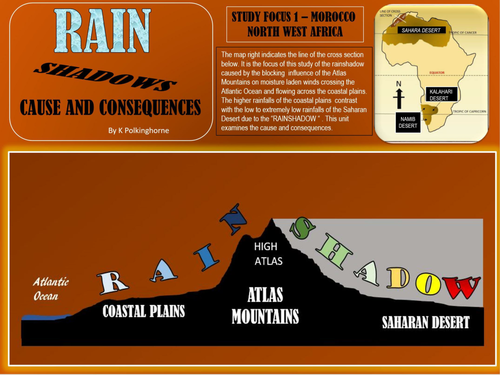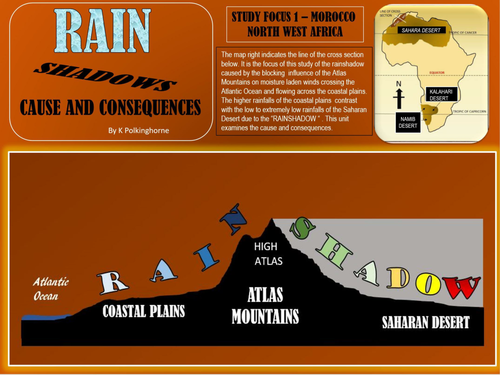



Rainshadows are common. They occur in landscapes where moisture laden air is forced to rise over physical barriers - mountains and hills. This sets in motion changes in atmospheric conditions which provide contrasts between areas on the incoming side (windward) and the interior areas (leeward side). By understanding the basic mechanism of rainshadows students can begin to understand some of the consequences - such as changes in rainfall and temperature. These variations in turn assist in recognising environmental changes and land use variations in areas affected by rainshadows. One clear example is the rainshadow area in the leeward area of the Atlas Mountains of Morocco. Here, due to the height and extent of the Atlas Mountains, the changes in climate are considerable. The second study is of a similar but less extreme impact of the rainshadow cause by the Mount Lofty Ranges in South Australia. Here the rainshadow influence has connection to the day to day weather reporting. By cross section, recognise the cause and consequences of rainshadows. The attachments provide ample opportunity for worksheet and activity. At a basic level this unit could be covered in Lower Secondary levels. The more complex meteorology is aimed at more senior Secondary levels. There's much more to rainshadows than you might think.
Something went wrong, please try again later.
Report this resourceto let us know if it violates our terms and conditions.
Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.
£0.00