Bundle
Acids, Bases & Buffers (OCR)
10 Full Lesson Bundle + BONUS lesson on Acids, bases & buffers. This bundle covers the OCR A Level Chemistry specification. Please review the learning objectives below.
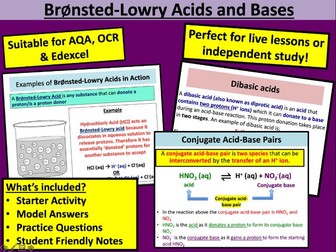
Lesson 1: Bronsted-Lowry Acid and Bases
To describe the difference between a BrØnsted Lowry acid and base
To identify conjugate acid-base pairs
To explain the difference between monobasic, dibasic and tribasic acids
To understand the role of H+ in the reactions of acids with metals and bases (including carbonates, metal oxides and alkalis), using ionic equations
Lesson 2: Strong Acids & The pH Scale
To calculate the pH of a strong acid
To convert between pH and [H+(aq)]
To apply the relationship between pH and [H+(aq)] to work out pH changes after dilution
**Lesson 3 - The Acid Dissociation Constant **
To understand the acid dissociation constant, Ka, as the extent of acid dissociation
To know the relationship between Ka and pKa
To convert between Ka and pKa
Lesson 4- pH of weak acids
To recall the expression of pH for weak monobasic acids
To calculate the pH of weak monobasic acids using approximations
To analyse the limitations of using approximations to Ka related calculations for ‘stronger’ weak acids
Lesson 5 - The ionic product of water
To recall the expression for the ionic product of water, Kw (ionisation of water)
To calculate the pH of strong bases using Kw
To apply the principles for Kc, Kp to Kw
Lesson 6-9 - Buffer Solutions (3 part lesson)
Part 1: Explaining How Buffer Solutions Work
To know a buffer solution is a system that minimises pH changes on addition of small amounts of an acid or base
To describe how a buffer solution is formed using weak acids, salts and strong alkalis
To explain the role of the conjugate acid-base pair in an acid buffer solution such as how the blood pH is controlled by the carbonic acid–hydrogencarbonate buffer system
Part 2: Buffer Solution Calculations (Part 1)
To calculate the pH of a buffer solution containing a weak acid and the salt of a weak acid by using the Ka expression and pH equation
To calculate equilibrium concentrations, moles or mass of the components of a weak acid-salt of a weak acid buffer solution
Part 3: Buffer Solution Calculations (Part 2)
To calculate the pH of a weak acid-strong alkali buffer solution
To calculate equilibrium concentrations, moles or mass of the components of a weak acid- strong alkali buffer solution
BONUS Lesson 9 : Revision on Buffer Solutions
To review how to calculate the pH of a buffer solution containing a weak acid and a strong alkali
To review how to calculate the pH of a buffer solution containing a weak acid and the salt of the weak acid
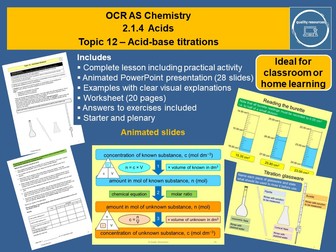
Lesson 10- Neutralisation & Titration Curves
To interpret titration curves of strong and weak acids and strong and weak bases
To construct titration curve diagrams of strong and weak acids and strong and weak bases
Lesson 11- pH indicators & Titration Curves
To explain indicator colour changes in terms of equilibrium shift between the HA and A- forms of the indicator
To explain the choice of suitable indicators given the pH range of the indicator
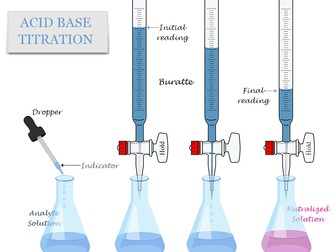
To describe an experiment for creating a titration curve
Declaimer: Please refrain from purchasing this popular resource for an interview lesson or a formal observation. This is because planning your own lessons including using your own lesson PowerPoints is a fundamental skill of a qualified/unqualified teacher that will be reviewed during these scenarios outlined above