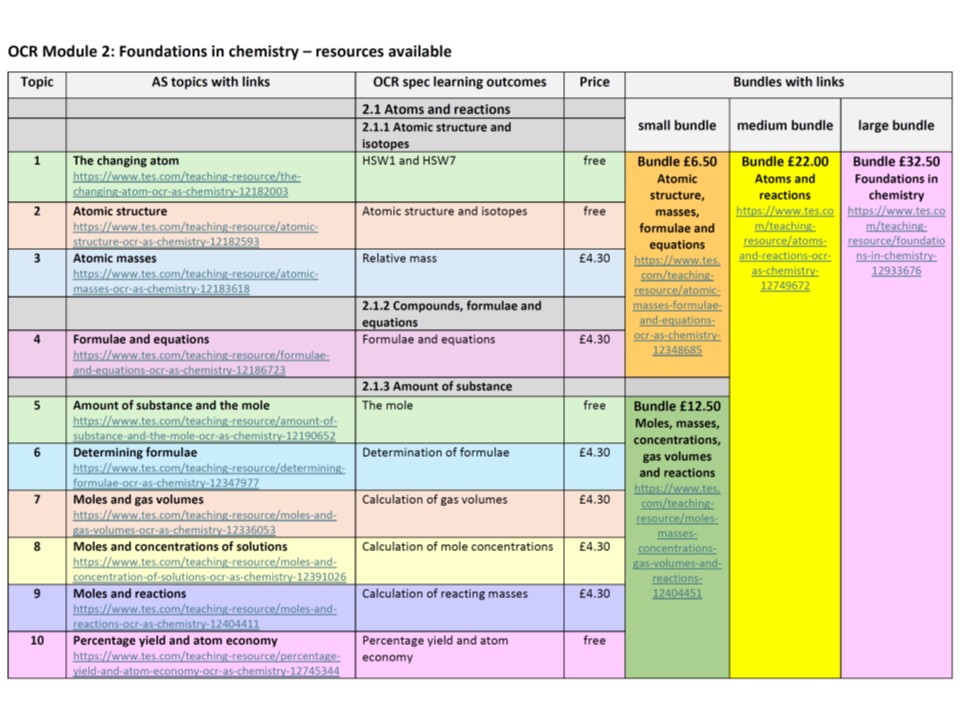
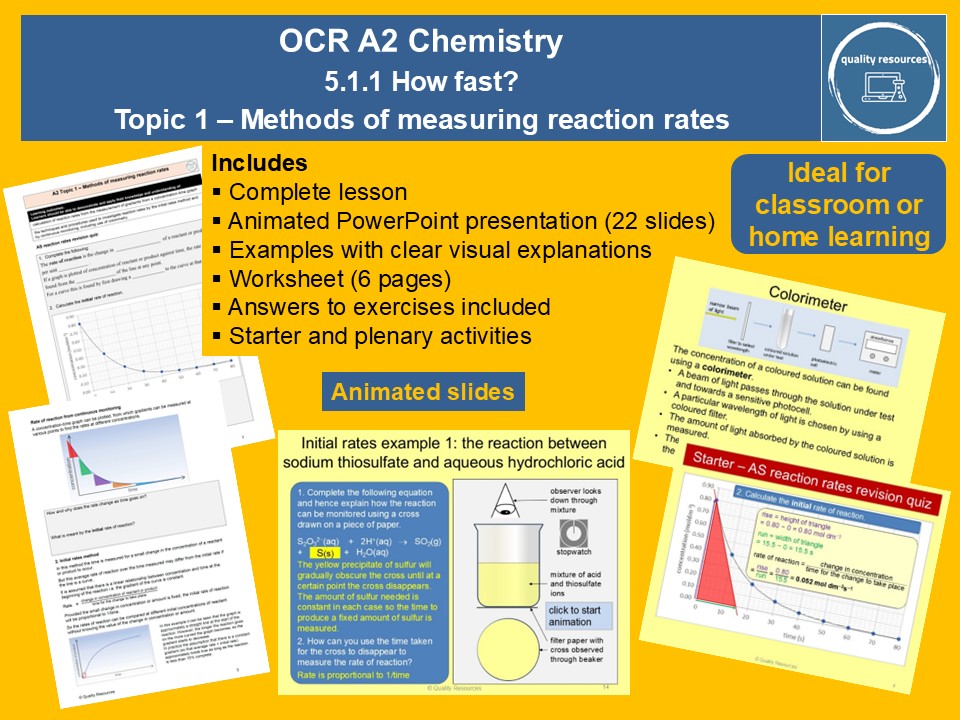
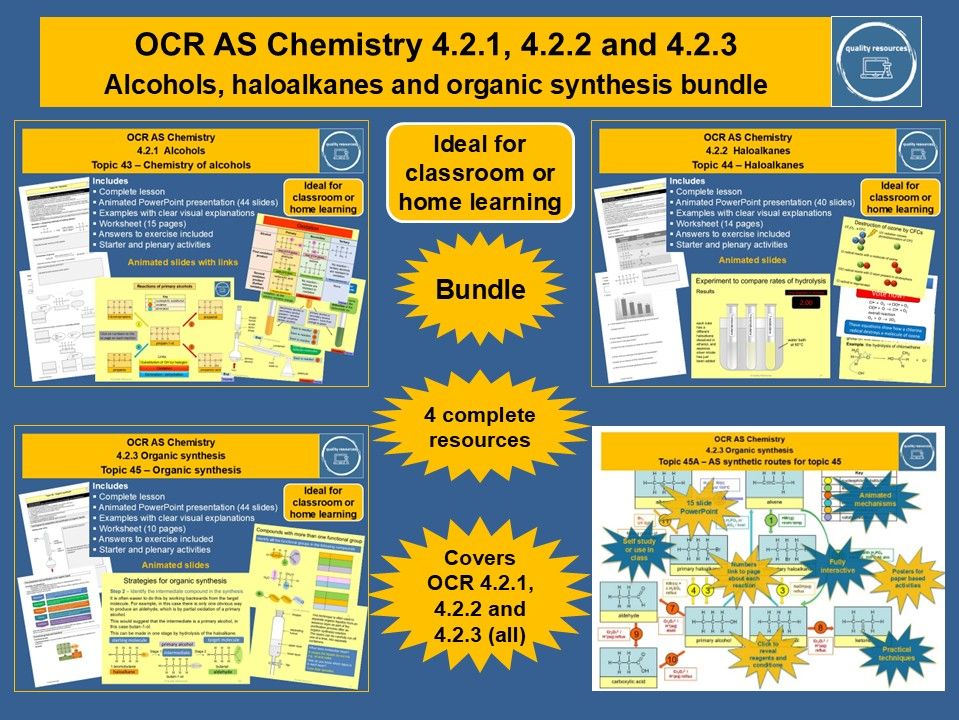
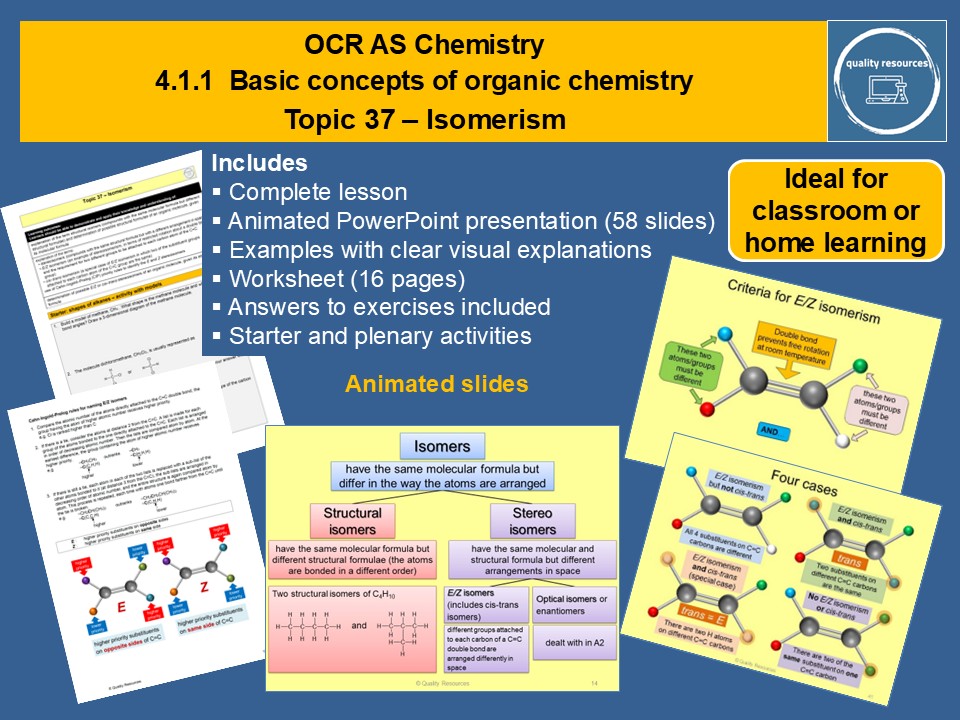
Quality Resources Shop
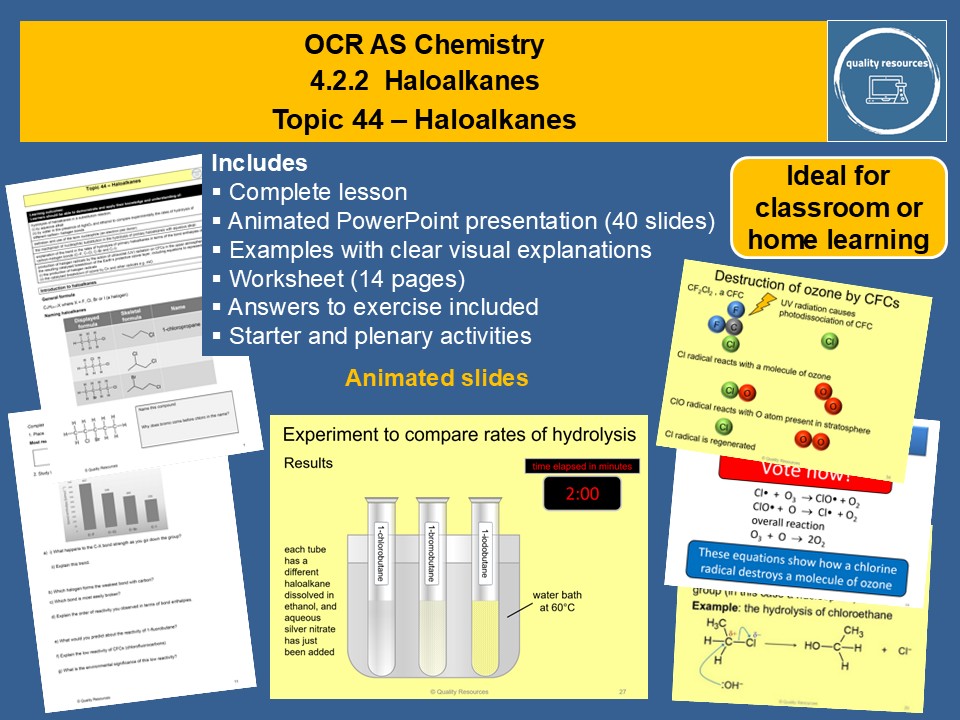
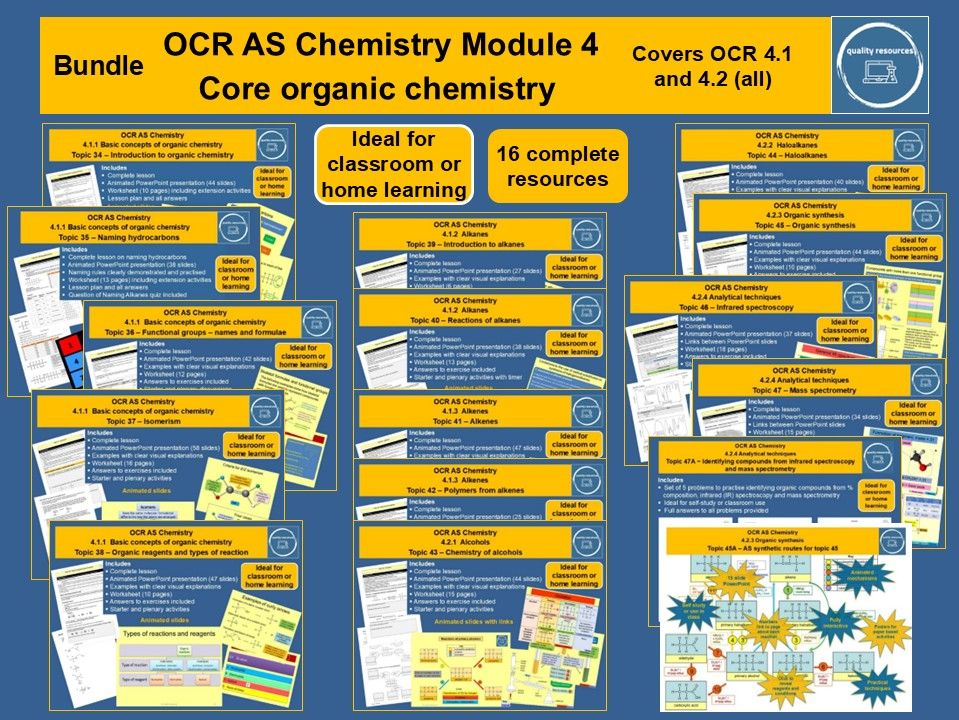
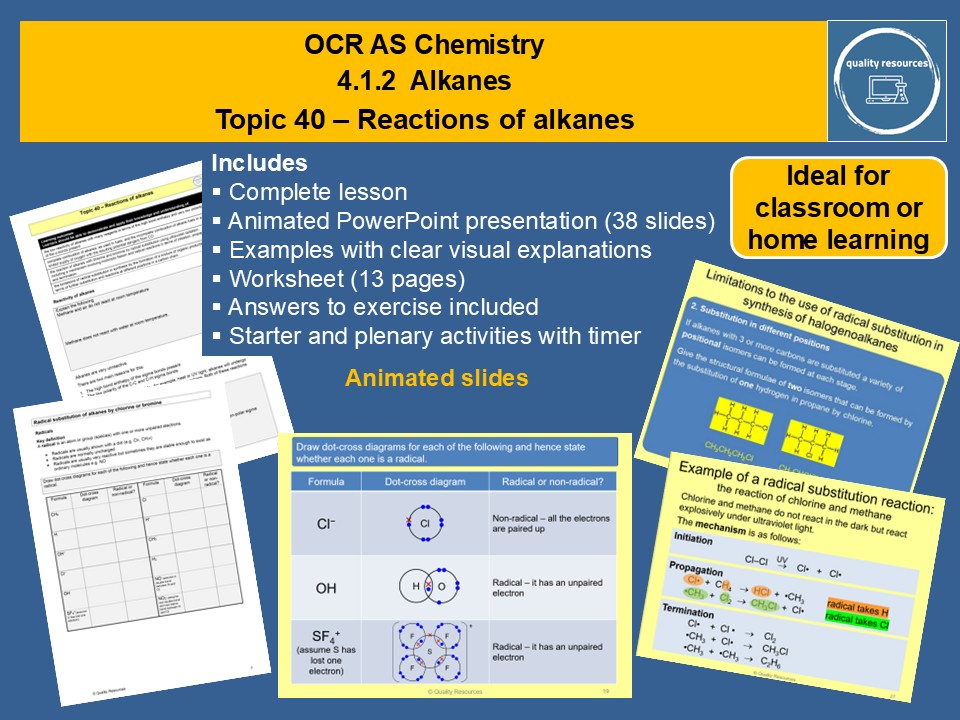
I am a very experienced chemistry teacher and have produced many quality resources which have been extensively tested in the classroom. My resources aim to engage the students and lighten the planning load for the teacher. A distinctive feature is the use of unique images, often animated, to explain concepts. The resources include interactive PowerPoints, activities and games, quizzes, worksheets with answers and exam style questions. Please review my resources!