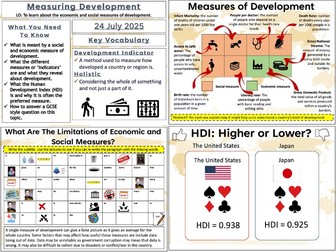
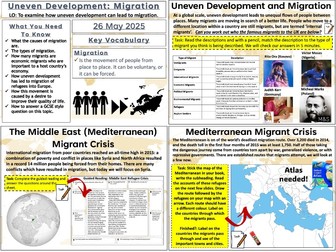
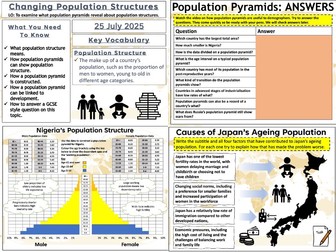
Urbanisation: An Increasingly Urban World
AQA GCSE Geography lesson for the new specification Unit 2A: In this lesson we look at the increasing number of the global population living in urban areas.
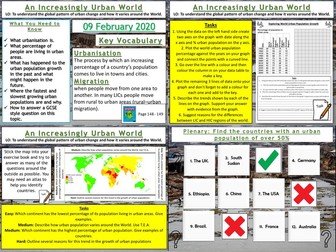
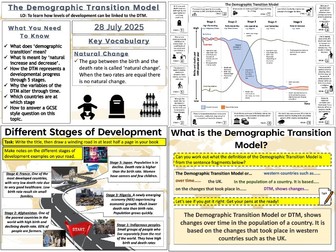
We start with a quick quiz on global populations and a video to put global population increase into context for the pupils. We then look at how urbanisation varies around the world by plotting data on a graph. The pupils then describe the trends they have found.
We then look at a map of the urban populations around the world and the pupils can tackle several different questions depending on ability. We then discuss how these patterns might be explained. We then answer a GCSE-style question looking at the percentage of people living in urban areas on different continents using a bar chart. The pupils have guidance on how to answer the question if needed. We finish with a plenary quiz where the pupils have to find the countries with an urban population of over 50%.
In a nutshell lesson includes:
Quiz starter
Video clip
Graph plotting exercise with questions
Map interpretation task
GCSE-style question using graph with guidance
Plenary quiz.
Hope this saves you some valuable planning time.
https://www.tes.com/teaching-resources/shop/markthegeographer