
Staff training poster on Vestibular Input
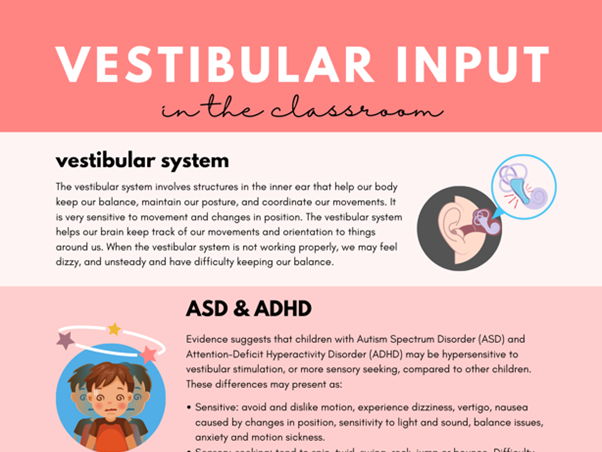
Vestibular input refers to sensory information received by the vestibular system, which is located within the inner ear. This system plays a crucial role in helping individuals maintain balance, posture, and spatial orientation.
The vestibular system detects motion, gravity, and changes in head position, sending signals to the brain about the body’s movement and orientation in space. This information is essential for coordinating movements, stabilising gaze, and maintaining equilibrium.
Vestibular input can come from various sources, including:
Head Movement: Turning the head, tilting it sideways, or nodding up and down all provide vestibular input.
Linear Movement: Walking, running, jumping, or riding in a vehicle all involve linear movement that stimulates the vestibular system.
Rotational Movement: Spinning, twirling, or rotating the body activates the vestibular system’s response to angular motion.
Gravity: Changes in posture, such as sitting, standing, or lying down, also influence the vestibular system’s perception of gravitational forces.
For individuals with sensory processing difficulties or vestibular dysfunction, providing appropriate vestibular input through activities like swinging, rocking, or balance exercises can help regulate arousal levels, improve attention, and enhance overall sensory integration.
Something went wrong, please try again later.
This resource hasn't been reviewed yet
To ensure quality for our reviews, only customers who have purchased this resource can review it
Report this resourceto let us know if it violates our terms and conditions.
Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.