


This fully-resourced lesson describes how Mycobacterium tuberculosis and human immunodeficiency virus infect human cells and cause symptoms. The PowerPoint and accompanying resources have been designed to cover point 6.6 in unit 4 of the Edexcel International A-level Biology specification and ties in closely with the previous lesson where the structure of bacteria and viruses were compared.
The lesson begins by ensuring that students recognise that TB is caused by the infection of a species of bacteria known as Mycobacterium tuberculosis and they will challenged to use their knowledge of scientific classification to recall that this pathogen is found in the mycobacteria genus. At this point, the students are told that the cell walls of this genus contain mycolic acids and later in the lesson they will have to work out that this specialist feature enables this pathogen to survive phagocytosis. A series of exam-style questions will challenge their knowledge of the respiratory and immune systems as they can understand how the bacterium travels to the alveoli where it is engulfed by a macrophage. Key terms like granuloma and necrosis are introduced and the sequence of events that occur following the formation of this aggregate of cells is described.
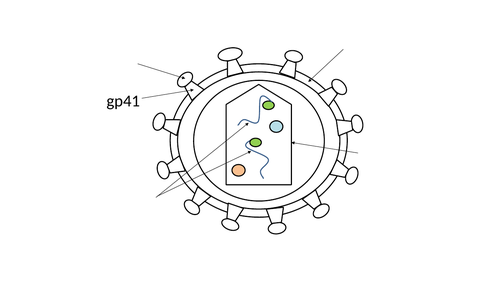
The structure of viruses was covered during the previous lesson, so this next part of the lesson starts by challenging the students to recall the capsid, genetic material in the form of viral RNA and the lipid envelope. At this point, the students are introduced to gp120, the glycoprotein which is exposed on the surface of the lipid envelope, as this structure is critical for the entry of the virus into host cells. Students will annotate a basic diagram of HIV with these four structures which also has gp41 labelled. A quick quiz competition introduces the names of the enzymes found inside the capsid
Moving forwards, the main task of this part of the lesson describes how HIV binds to the helper T cells, injects its capsid and integrates its DNA into the host’s genome in order to replicate to form virus particles (virions). Students are guided through the formation of a detailed answer about the mechanism of HIV and have to input key terms and structures where information is missing. Students will learn that the increase in the number of virus particles and a decrease in helper T cells and other immune cells results in infections like TB and by opportunistic pathogens and that this stage is recognised as AIDS
Something went wrong, please try again later.
This resource hasn't been reviewed yet
To ensure quality for our reviews, only customers who have purchased this resource can review it
Report this resourceto let us know if it violates our terms and conditions.
Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.