

This lesson describes the adaptations of gas exchange surfaces in single-celled organisms, insects, bony fish and dicotyledonous plants. The PowerPoint and accompanying worksheets are part of the first lesson in a series of 6 lessons that have been designed to cover the detail of point 3.2 (Gas exchange) of the AQA A-level Biology specification.
The lesson has been intricately planned to challenge the students on their understanding of the surface area to volume ratio (as covered in the previous lesson) and to make direct links to upcoming lessons on gas exchange and transport systems in humans. The lesson begins by explaining that single-celled organisms are able to diffuse oxygen and carbon dioxide across their body surface but that as organisms increase in size and their SA/V ratio decreases, they need adaptations at their gas exchange surfaces to be able to obtain the oxygen to meet their metabolic demands. This leads into the next part of the lesson which describes the roles of the following structures in insects and bony fish:
- spiracles, tracheae, tracheoles and tracheole fluid
- operculum, gill arch, gill filaments and lamellae
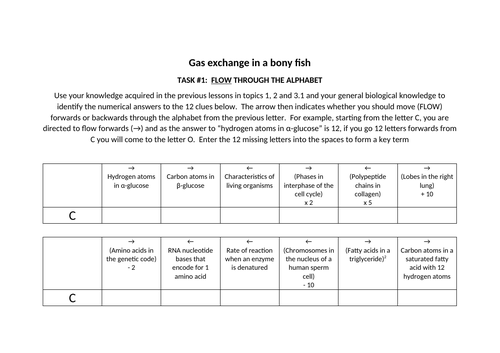
The next task challenges the students to use their knowledge of topics 1 and 2 to come up with the letters that form the key term, countercurrent flow. This is a key element of the lesson and tends to be a principle that is poorly understood, so extra time is taken to explain the importance of this mechanism. Students are shown two diagrams, where one contains a countercurrent system and the other has the two fluids flowing in the same direction, and this is designed to support them in recognising that this type of system ensures that the concentration of oxygen is always higher in the oxygenated water than in the blood in the lamellae.
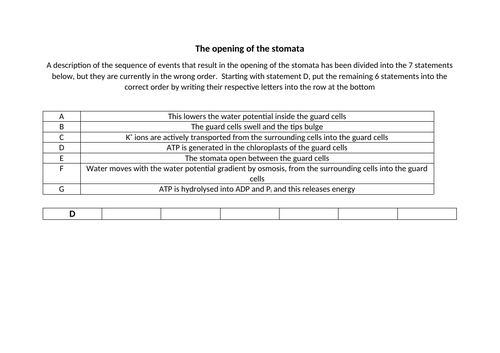
The final part of the lesson describes the role of the stomata and the mesophyll cells in the gas exchange of a dicotyledonous plant. Students will learn that guard cells contain chloroplasts which generate ATP and then they are challenged to order a series of statements to form a description of the events that result in the opening of the stomata. The differing structures of the spongy mesophyll and palisade mesophyll cells are then considered before the students are challenged to explain how carbon dioxide moves through the leaf after entering via the stomata and then how water vapour and oxygen leave. Clear links are made to the loss of water vapour by transpiration so students are prepared for the lessons covering this biological process later in topic 3.
Get this resource as part of a bundle and save up to 35%
A bundle is a package of resources grouped together to teach a particular topic, or a series of lessons, in one place.
Topics 3.1, 3.2 & 3.3 (AQA A-level Biology)
This bundle contains 7 lessons which are highly detailed and cover the following points in the surface area to volume ratio, gas exchange and digestion and absorption topics of the AQA A-level Biology specification: * The relationship between the size of an organism or structure and its surface area to volume ratio * The development of systems in larger organisms as adaptations that facilitate exchange as this ratio reduces * Adaptations of gas exchange surfaces in single-celled organisms, insects, bony fish and in the leaf of a dicotyledonous plant * The gross structure of the human gas exchange system * The essential features of the alveolar epithelium over which gas exchange takes place * Ventilation and the exchange of gases in the lungs * Digestion in mammals of carbohydrates, proteins and lipids * Mechanisms for the absorption of the products of digestion by cells lining the ileum If you would like to sample the quality of lessons in this bundle, then download the alveolar epithelium and absorption in the ileum lessons as these have been uploaded for free
Topic 3.2: Gas exchange (AQA A-level Biology)
This bundle contains 4 lessons which cover the following content that's set out in topic 3.2 (Gas exchange) of the AQA A-level Biology specification: * Adaptations of gas exchange surfaces as shown by the gas exchange in single-celled organisms, insects, bony fish and the leaves of dicotyledonous plants * The gross structure of the human gas exchange system * The essential features of the alveolar epithelium as a surface over which gas exchange takes place * The mechanism of breathing All of the lessons are detailed and have been intricately planned to contain a wide range of tasks that will challenge the students on their understanding of the current topic as well as their recall of knowledge from previously-covered topics. In this way, the students are encouraged to make links between biological processes in different topics so they are prepared for assessment questions which do just that. Lessons covering topics 3.1, 3.3 and 3.4 are also uploaded
Topic 3: Organisms exchange substances with their environment (AQA A-level Biology)
This lesson bundle contains 17 detailed and fully-resourced lessons which cover the following specification points in topic 3 of the AQA A-level Biology specification: Topic 3.1 * The relationship between the size of an organism or structure and its surface area to volume ratio * The development of systems in larger organisms as adaptations that facilitate exchange as this ratio reduces Topic 3.2 * Adaptations of gas exchange surfaces as shown by gas exchange in single-celled organisms, insects, bony fish and the leaves of dicotyledonous plants * The gross structure of the human gas exchange system * The essential features of the alveolar epithelium as a surface over which gas exchange takes place * The mechanism of breathing to include the role of the diaphragm and the intercostal muscles Topic 3.3 * During digestion, large molecules are hydrolysed to smaller molecules * Digestion in mammals by amylases, disaccharidases, lipase, endopeptidases, exopeptidases and dipeptidases * Mechanisms for the absorption of the products of digestion by cells lining the ileum of mammals Topic 3.4.1 * The structure and role of haemoglobin in the loading, transport and unloading of oxygen * The effects of carbon dioxide concentration on the dissociation of oxyhaemoglobin * The general pattern of blood circulation in a mammal * The gross structure of the human heart * Pressure and volume changes and valve movements during the cardiac cycle * The structure of the arteries, arterioles and veins * The formation of tissue fluid and its return to the circulatory system Topic 3.4.2 * Xylem as the tissue that transports water * The cohesion-tension theory of water transport * Phloem as the tissue that transports organic substances in plants * The mass flow hypothesis for the mechanism of translocation in plants If you would like to sample the quality of the lessons included in this bundle, then download the following lessons which have been uploaded for free Alveolar epithelium Absorption in the ileum Arteries, arterioles and veins Formation of tissue fluid Translocation
Something went wrong, please try again later.
This resource hasn't been reviewed yet
To ensure quality for our reviews, only customers who have purchased this resource can review it
Report this resourceto let us know if it violates our terms and conditions.
Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.