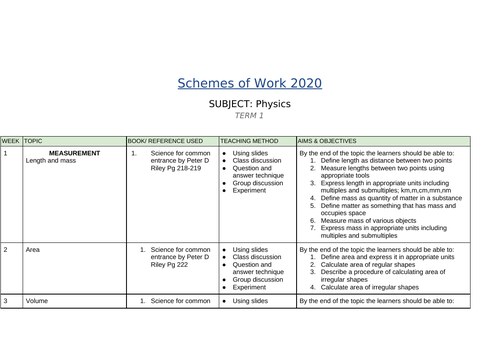
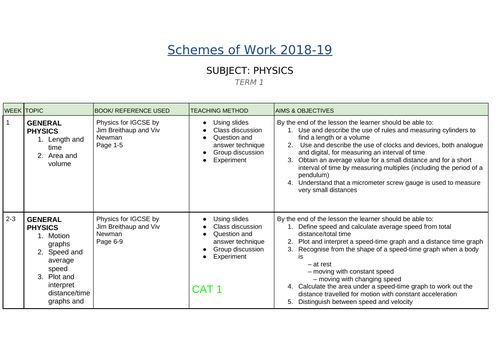
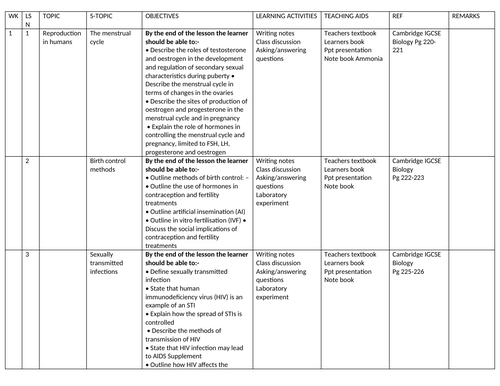
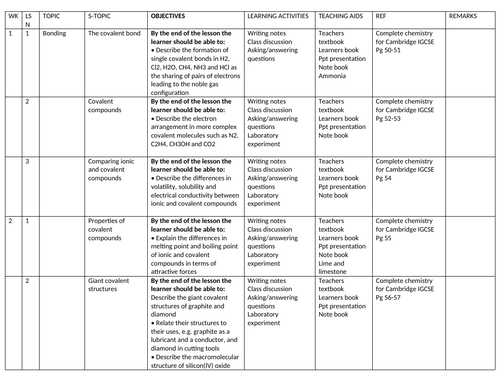
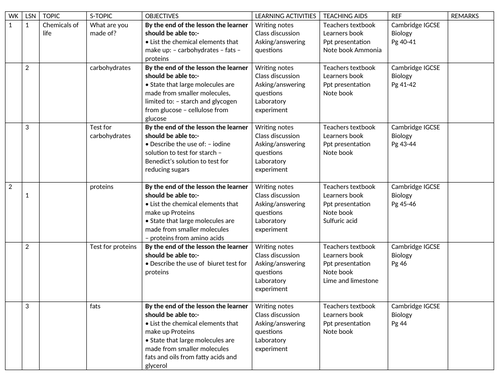
SCHEMES OF WORK AND TEACHING MATERIALS SHOP
A teacher teaching Chemistry and Biology. Mr. Mathai Jackson is known for his hard work in everything he does while teaching. He has been teaching IGCSE and A level for the past 15 years, thus has accumulated great teaching wealth.