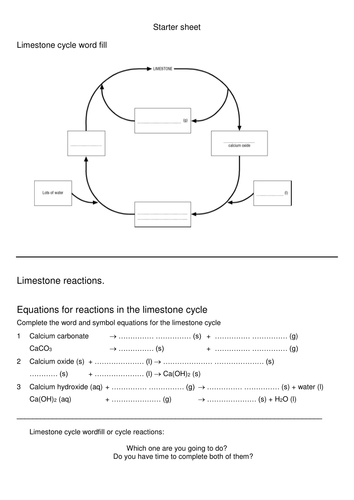
TopTenTeacher-Science.
Resources here for IBDP and A-Level Chemistry, as well as Edexcel IGCSE and AQA GCSE Chemistry. I have a huge range of resources for 11-14 so ask if you need something specific. After teaching for 13 years in the UK and in international schools I have built up quite a selection of teaching resources. You can also visit my site www.toptenteacher.co.uk.