



New version - updated to complete lesson!
If you have already paid for this resource you can download it again without extra payment.
My resources now cover the whole of OCR AS Chemistry.
Each download includes a list of all available lessons and bundles.
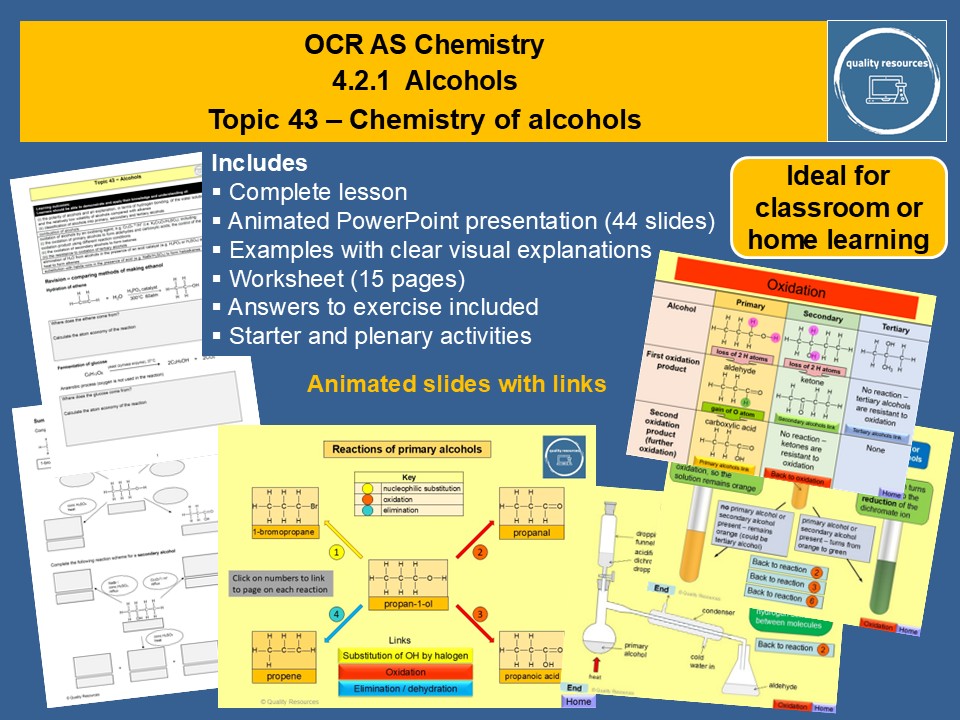
This complete year 12 lesson on alcohols covers OCR section 4.2.1 (alcohols). Content includes the physical and chemical properties of alcohols, as well as naming and classification. The resource features a 44 slide animated PowerPoint that illustrates and explains the concepts in a lively and visual way. Many of the PowerPoint slides contain links to other slides, to enable easy navigation and to emphasise links between the types of alcohol and the types of reaction. As well as pages devoted to each of the main types of reaction (substitution, oxidation and elimination), primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols each have a page with a clear chart of numbered reactions, where each number is linked to a page detailing that reaction. Information given includes type of reaction, reagents and conditions and an equation, as well as key definitions. In addition the reactions have an animated mechanism or structural equation. There are links to pages describing and explaining practical techniques, where relevant.
There is a starter and a plenary activity as well as a 15 page workbook. Exam tips and answers to the exercises are provided. Ideal for the classroom or blended learning, this resource could be used as an introduction to the topic, or for revision, extension or consolidation.
This lesson is part of a series covering the OCR AS Chemistry specification and relates to the following part of the specification:
Module 4 – Core organic chemistry
Part 2 – Alcohols, haloalkanes and analysis
4.2.1 Alcohols
Content covered
• Comparing methods of making ethanol
• Naming alcohols
• Physical properties of alcohols, in terms of hydrogen bonding
• Primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols
• Substitution reaction of alcohols
• Oxidation of alcohols
• Elimination (dehydration) reaction of alcohols
• Reactions of primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols
• Animated mechanisms
• Reaction classification
• Reagents and conditions
• Structural equations
• Key definitions
• Heating under reflux
• Distillation to prevent complete oxidation
Duration: 1-2 lessons and/or independent study
Please review
Links
Previous lesson – Topic 42 − Polymers from alkenes
https://www.tes.com/teaching-resource/polymers-from-alkenes-ocr-as-chemistry-13316815
Next lesson – Topic 44 − Haloalkanes
https://www.tes.com/teaching-resource/haloalkanes-ocr-as-chemistry-13324028
Get this resource as part of a bundle and save up to 43%
A bundle is a package of resources grouped together to teach a particular topic, or a series of lessons, in one place.
Core organic chemistry bundle
This bundle covers all of the OCR A level chemistry specification section 4.1 (basic concepts and hydrocarbons) and 4.2 (alcohols, haloalkanes and analysis). The resources included are: - Introduction to organic chemistry - Naming hydrocarbons (includes quiz – A Question of naming alkanes) - Functional groups – names and formulae - Isomerism - Organic reagents and types of reaction - Introduction to alkanes - Reactions of alkanes - Alkenes - Polymers from alkenes - Chemistry of alcohols - Haloalkanes - Organic synthesis - AS synthetic routes - Infrared spectroscopy - Mass spectrometry - Identifying compounds from infrared and mass spectra Each topic includes a fully interactive PowerPoint including starter, group activities, questions and plenary along with a worksheet. Answers to all exercises are provided. Some of the resources include a PowerPoint quiz and all are ideal for classroom or home learning. This bundle is part of a series covering the OCR AS Chemistry specification and relates to the following sections: Module 4– Core organic chemistry Part 1 – Basic concepts and hydrocarbons (all) Part 2 - Alcohols, haloalkanes and analysis (all) **Please review!** **Content covered: Introduction to organic chemistry** • Why carbon is special • Bonding in organic compounds • Different types of formulae • Types of organic compounds • Functional groups and homologous series **Naming hydrocarbons** • Application of IUPAC rules of nomenclature for systematically naming organic compounds • Naming alkanes and cycloalkanes • Naming branched alkanes • Naming alkenes and branched alkenes Quiz – A Question of naming alkanes **Functional groups – names and formulae** • Application of IUPAC rules of nomenclature for systematically naming organic compounds • Practice naming organic compounds including those with functional groups • Revision of empirical and molecular formula and how to calculate them • Formulae of compounds with functional groups Displayed formula Structural formula Skeletal formula **Isomerism** • Shapes of alkanes (with model building) • Definitions of structural isomers, stereoisomers, E/Z isomers and cis-trans isomers • Classification of isomers with examples • Structural isomers including chain, position and functional group isomers • Shapes of alkenes (with model building) • Restricted rotation around the C=C double bond • Stereoisomers – E/Z and cis-trans isomers • Animated illustrations of E/Z isomers • Criteria for E/Z isomerism and for cis-trans isomerism with examples and learning check • Cahn-Ingold-Prelog rules for naming E/Z isomers with examples **Organic reagents and types of reaction** • Ways of breaking covalent bonds Homolytic fission Heterolytic fission • Types of organic reagents and their reactions Nucleophiles Electrophiles Radicals • Introduction to mechanisms • Curly arrows • Types of reaction Addition Substitution Elimination • Classification of reactions **Introduction to alkanes** * Sources and uses of alkanes * Definitions of fossil fuels and crude oil * Uses of alkanes as fuels * Bonding in alkanes * Formation and rotation of sigma bonds * Shapes of alkanes * Intermolecular forces in alkanes in terms of non-polar molecules * Melting and boiling points of alkanes in terms of London forces * Effect of chain length and branching on London forces **Reactions of alkanes** * Reactivity of alkanes * Combustion of alkanes – complete and incomplete * Balancing combustion equations * Radicals and dot-and-cross diagrams * Radical chain reactions * Radical substitution of alkanes by halogens * Mechanism including initiation, propagation and termination * Limitations to the use of radical substitution in synthesis of halogenoalkanes **Alkenes** * Structure and reactivity of alkenes * The nature of the double bond – sigma and pi bonds * Explanation of restricted rotation around C=C * Shape of ethene in terms of electron pair repulsion theory * Addition reactions of alkenes * Reactions of ethene and propene including addition of halogens, steam, hydrogen halides and hydrogen * Test for alkenes with aqueous bromine * Catalytic addition of hydrogen - mechanism * Margarine manufacture * Definition of electrophile * Electrophilic addition mechanism * Addition of HX to unsymmetrical alkenes - Markownikoff’s rule and explanation **Polymers from alkenes** * Meaning of the terms addition polymer and monomer * the formation of poly(ethene) * General equation for polymer formation * Identifying the monomer from the repeat unit of the monomer * Disposal of waste polymers by recycling, cracking and combustion * Bioplastics * Biodegradable polymers * Photodegradable polymers **Chemistry of alcohols** * Comparing methods of making ethanol * Naming alcohols * Physical properties of alcohols, in terms of hydrogen bonding * Primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols * Substitution reaction of alcohols * Oxidation of alcohols * Elimination (dehydration) reaction of alcohols * Reactions of primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols * Animated mechanisms * Reaction classification * Reagents and conditions * Structural equations * Key definitions **Haloalkanes** * Naming haloalkanes * Reactivity of haloalkanes general equation for polymer formation * Uses of haloalkanes * Nucleophilic substitution reactions of haloalkanes including hydrolysis * Mechanism of nucleophilic substitution * Experiment to compare rates of hydrolysis of different haloalkanes * Explaining the different rates of hydrolysis * Organohalogen compounds and the environment * Destruction of ozone by CFCs **Organic synthesis** * Revision of functional groups * Techniques for preparation and purification of organic liquids * Heating under reflux * Distillation * Separation of immiscible liquids using a separating funnel * Use of drying agents * Stages in the preparation and purification of an organic liquid * Tests for functional groups * Compounds with more than one functional group * Strategies for organic synthesis with examples **AS synthetic routes** * AS synthetic routes * Animated mechanisms * Key definitions * Heating under reflux * Distillation * Reaction classification * Reagents and conditions * Structural equations **Infrared spectroscopy** * Introduction to spectroscopy linked to the electromagnetic spectrum * Meaning of wavenumber and transmittance * Molecular vibrations * Bond stretching * Fingerprint region of spectrum * Types and shapes of peaks * Infrared and global warming * The greenhouse effect and greenhouse gases * Interpreting the infrared spectrum * Examples of IR spectra with animated explanation linking peaks to structure * Uses of infrared spectroscopy **Mass spectrometry** * Animated diagram and description of a mass spectrometer * Meaning of m/z * Relative intensity * Base peak * Molecular ion * M+1 peak * Fragments * Interpreting the mass spectrum * Mass spectrum of ethanol * Animations of formation of fragments from ethanol * Summary of fragments for ethanol * Examples of mass spectra with animated explanation linking peaks to structure * Interpretation of mass spectrum of unknown compound leading to its identification **Identifying compounds from infrared and mass spectra** * Calculating empirical formula from % composition * Calculating molecular formula from empirical formula and molar mass, using the molecular ion peak on the mass spectrum * Using the infrared (IR) spectrum to identify bond stretches and hence functional group(s) present * Drawing structural formulae consistent with the molecular formula and IR data * Using mass spectrum to distinguish between the suggested structural formulae * Identifying fragments in the mass spectrum
Alcohols, haloalkanes and analysis bundle OCR AS Chemistry
This bundle covers all of the OCR A level chemistry specifications section 4.2 (alcohols, haloalkanes and analysis) The resources included are: - chemistry of alcohols - haloalkanes - organic synthesis - AS synthetic routes - infrared spectroscopy - mass spectrometry - identifying compounds from infrared and mass spectra Most of the resources include a fully interactive PowerPoint including starter, group activities, questions and plenary along with a worksheet. Many of the PowerPoint slides contain links to other slides, to enable easy navigation and to emphasise links between different aspects. Some of the resources include a PowerPoint quiz and all are ideal for classroom or home learning. The synthetic routes resource covers AS organic synthetic routes through a 15 slide interactive PowerPoint that is based on a clear chart of numbered synthetic routes, where each number is linked to a page detailing that reaction. Information given includes type of reaction, reagents and conditions and an equation, as well as key definitions. In addition most reactions have an animated mechanism or structural equation. There are links to pages describing and explaining practical techniques, where relevant. Also included is a resource consisting of a set of five problems to practise identifying organic compounds from % composition, infrared (IR) spectroscopy and mass spectrometry. Full answers to all exercises are provided. This bundle is part of a series covering the OCR AS Chemistry specification and relates to the following sections: Module 4– Core organic chemistry Part 2 –Alcohols, haloalkanes and analysis (all) **Please review!** **Content covered: Chemistry of alcohols** • Comparing methods of making ethanol • Naming alcohols • Physical properties of alcohols, in terms of hydrogen bonding • Primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols • Substitution reaction of alcohols • Oxidation of alcohols • Elimination (dehydration) reaction of alcohols • Reactions of primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols • Animated mechanisms • Reaction classification • Reagents and conditions • Structural equations • Key definitions **Haloalkanes** • Naming haloalkanes • Reactivity of haloalkanes general equation for polymer formation • Uses of haloalkanes • Nucleophilic substitution reactions of haloalkanes including hydrolysis • Mechanism of nucleophilic substitution • Experiment to compare rates of hydrolysis of different haloalkanes • Explaining the different rates of hydrolysis • Organohalogen compounds and the environment • Destruction of ozone by CFCs **Organic synthesis** • Revision of functional groups • Techniques for preparation and purification of organic liquids • Heating under reflux • Distillation • Separation of immiscible liquids using a separating funnel • Use of drying agents • Stages in the preparation and purification of an organic liquid • Tests for functional groups • Compounds with more than one functional group • Strategies for organic synthesis with examples **AS synthetic routes** • AS synthetic routes • Animated mechanisms • Key definitions • Heating under reflux • Distillation • Reaction classification • Reagents and conditions • Structural equations **Infrared spectroscopy** • introduction to spectroscopy linked to the electromagnetic spectrum • meaning of wavenumber and transmittance • molecular vibrations • bond stretching • fingerprint region of spectrum • types and shapes of peaks • infrared and global warming • the greenhouse effect and greenhouse gases • interpreting the infrared spectrum • examples of IR spectra with animated explanation linking peaks to structure • uses of infrared spectroscopy **Mass spectrometry** • animated diagram and description of a mass spectrometer • meaning of m/z • relative intensity • base peak • molecular ion • M+1 peak • fragments • interpreting the mass spectrum • mass spectrum of ethanol • animations of formation of fragments from ethanol • summary of fragments for ethanol • examples of mass spectra with animated explanation linking peaks to structure • interpretation of mass spectrum of unknown compound leading to its identification **Identifying compounds from infrared and mass spectra** • Calculating empirical formula from % composition • Calculating molecular formula from empirical formula and molar mass, using the molecular ion peak on the mass spectrum • Using the infrared (IR) spectrum to identify bond stretches and hence functional group(s) present • Drawing structural formulae consistent with the molecular formula and IR data • Using mass spectrum to distinguish between the suggested structural formulae • Identifying fragments in the mass spectrum
Alcohols, haloalkanes and organic synthesis bundle OCR AS Chemistry
This bundle covers all of the OCR A level chemistry specifications section 4.2.1 (alcohols), 4.2.2 (haloalkanes) and 4.2.3 (organic synthesis) The resources included are: - chemistry of alcohols - haloalkanes - organic synthesis - AS synthetic routes The first three resources include a fully interactive PowerPoint including starter, group activities, questions and plenary along with a worksheet. Answers to all exercises are provided. Some of the resources include a PowerPoint quiz and all are ideal for classroom or home learning. The final resource covers AS organic synthetic routes through a 15 slide interactive PowerPoint that is based on a clear chart of numbered synthetic routes, where each number is linked to a page detailing that reaction. Information given includes type of reaction, reagents and conditions and an equation, as well as key definitions. In addition most reactions have an animated mechanism or structural equation. There are links to pages describing and explaining practical techniques, where relevant. This bundle is part of a series covering the OCR AS Chemistry specification and relates to the following sections: Module 4– Core organic chemistry Part 2 –Alcohols, haloalkanes and analysis 4.2.1 (alcohols), 4.2.2 (haloalkanes) and 4.2.3 (organic synthesis) **Please review!** **Content covered:** **Chemistry of alcohols** • Comparing methods of making ethanol • Naming alcohols • Physical properties of alcohols, in terms of hydrogen bonding • Primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols • Substitution reaction of alcohols • Oxidation of alcohols • Elimination (dehydration) reaction of alcohols • Reactions of primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols • Animated mechanisms • Reaction classification • Reagents and conditions • Structural equations • Key definitions **Haloalkanes** • Naming haloalkanes • Reactivity of haloalkanes general equation for polymer formation • Uses of haloalkanes • Nucleophilic substitution reactions of haloalkanes including hydrolysis • Mechanism of nucleophilic substitution • Experiment to compare rates of hydrolysis of different haloalkanes • Explaining the different rates of hydrolysis • Organohalogen compounds and the environment • Destruction of ozone by CFCs **Organic synthesis** • Revision of functional groups • Techniques for preparation and purification of organic liquids • Heating under reflux • Distillation • Separation of immiscible liquids using a separating funnel • Use of drying agents • Stages in the preparation and purification of an organic liquid • Tests for functional groups • Compounds with more than one functional group • Strategies for organic synthesis with examples **AS synthetic routes** • AS synthetic routes • Animated mechanisms • Key definitions • Heating under reflux • Distillation • Reaction classification • Reagents and conditions • Structural equations **Links** Next topic Topic 46 – Infrared spectroscopy – OCR AS Chemistry https://www.tes.com/teaching-resource/infrared-ir-spectroscopy-ocr-as-chemistry-12315096 Next small bundle Analytical techniques https://www.tes.com/teaching-resource/resource-12325546
Something went wrong, please try again later.
I love this as a flip learning task for my AS, I would like arrow heads on the reaction arrows as my pupils got confused with which direction the electrons were going.
I would like to be able to save the pdf to my files then onto google.
Just what I was looking for thanks for sharing
Report this resourceto let us know if it violates our terms and conditions.
Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.