65Uploads
9k+Views
13k+Downloads
All resources

AQA: First World War 1894-1918 entire unit
These lessons have been designed to be easy to follow.
Lessons follow the AQA (BA) Conflict and tension: The First World War, 1894–1918 , and include the following 26 lessons
Part one: The causes of the First World War
1.01 The alliance system (2022, Q3)
1.02 Moroccan Crises (S1, Q3)
1.03 Crisis in the Balkans (2018, Q3)
1.04 Splendid isolation
1.05 Wilhelm foriegn policy (2022, Q1)
1.06 European rearmament
1.07 Slav nationalism and Austro-Serbian rivalry
1.08 Assassination
1.09 July Crisis
1.10 cause of WW1
Part two: The First World War: stalemate
2.01 Schlieffen Plan & Belgium
2.02 Trenches and Marne (2020, Q3)
2.03 military tactics and technology
2.04 Verdun
2.5 Somme (S2, Q2)
2.06 Passchendaele
2.07 Haig
2.8 Gallipoli (2018, Q1)
2.09 War at sea
Part three: Ending the war
3.01 Russia leaves (2019, Q1)
3.02 USA enters WW1 (S2, Q1)
3.03 tactics and technology (2019, Q2)
3.04 Ludendorff Offensive (2021, Q4; S2, Q3)
3.05 Hundred Days
3.06 end of WW1 (2022, Q2)
3.07 Cause of Germany’s defeat (2018, Q2; 2020, Q4)
The lessons use the Oxford Conflict and Tension: First World War 1894-1918 book (9780198429005); HOWEVER, there is an alternative for every time the textbook has been included. You will just need to print the reading sheets.
The lesson clearly displays where an exam question has been used and includes the mark scheme.
All comprehension activities have the answers included on the next slide.
Lessons include links to YouTube for engagement.

iGCSE Edexcel Cause and course of WW1 (A1)
This series of lessons follows the iGCSE Edexcel History, paper 2 (A1) The origins and course of the First World War, 1905–18.
18 content lessons plus two exam lessons.
Each lesson uses the textbook, but there are reading alternatives too.
Lessons follow the specification published by Edexcel and included:
1.1 The alliance system
1.2 Economic and imperial causes of war
1.3 Military causes of war
2.1 Moroccan Crises
2.2 Crises in the Balkans
2.3 Balkan nationalism and Serbian rivalry
2.4 Assassination to war
3.1 Schlieffen Plan and reasons for its failure
3.2 Trenches and reasons for deadlock
3.4 Somme
3.5 Passchendaele
3.6 Haig
4.1 German threat at North Sea
4.2 U-boats
4.3 Gallipoli (2 lessons)
5.1 Ludendorff Offensive
5.2 Hundred Days
5.3 Cause of Germany’s defeat
2 exam lessons
Lessons include relevant exam questions with mark schemes
There is a learning check list for the students
There is also a learning checklist that matches up specification topic with exam questions.
There are two lessons that focus on the examination.
o One for B question. Examples, work for students to mark and then one to complete.
o One for C question. Example answers, work for students to mark and then one to complete.

Reformation and religious transformation of England
This lesson covers three learning objectives
I will be able to recall key knowledge about Henry VIII.
I should be able to describe the transformation of England.
I might also be able to explain how far Henry VIII had changed England.
Lesson includes reading comprehension and self assessment.
There are three reading packs to choose from (reading ages of 13, 10, and 8). The self assessment is targeted at reading age 13, but this is easily swapped.
Final activity is a PEE paragraph to answer the question: how far was the Reformation a transformation?

How did Henry VIII gain wealth and power from the Reformation?
This lesson covers three learnign objectives:
I will b able to recall key information about Henry VIII’s break with Rome.
I should be able to describe how Henry VIII received wealth and power from his break with Rome.
I might also be able to explain how far wealth and power were causes of Henry VIII’s break with Rome.
Activity includes differentiated reading (reading ages 13, 10, and 8).
Self assessment activities included.
Final activity includes answer to the PEE paragraph: how far was wealth and power to blame for the break from Rome? The next slide includes peer assessment activities.

Henry VIII's break with Rome
This lesson covers three learning objectives:
I will be able to recall key information about Henry’s Great Matter
I should be able to describe how Henry VIII’s break from Rome was caused by his desire to marry Anne Boleyn.
I might also be able to explain how far Henry VIII’s break from Rome was caused by his desire to marry Anne Bolyn.
This lesson includes a reading comprehension activity that is self assessed. There are three packs to choose from (reading ages 13, 10, and 8). The self assessment is targeted at reading age 13. There is a worksheet that targets responsibility for the break from Rome.
The final activity is answering the PEE paragraph: who was to blame for the English Reformation?

Henry VIII's Great Matter
This lesson includes three learning objectives:
I will be able to recall key details about the Reformation
I should be able to describe what Henry VIII’s Great Matter was.
I might also be able to explain why Henry VIII divorced Rome.
This lesson includes links to engaging YouTube videos and reading. The reading is differentiated into three different packs that you can select (reading ages of 13, 10, and 8).
The final activity concludes with a PEE paragraph answering the question: why did Henry VIII divorce Rome? This is a peer assessment activity with examples of WWW and EBIs.

What was the Reformation?
This lesson covers three learning objectives:
I will be able to identify the values of a religious institution.
I should be able to describe what the Reformation was.
I might also be able to explain why the Reformation happened.
This lesson comes with three reading packs that are differentiated by reading age (reading ages of 13, 10, and 8). The self assessment in the lesson is connected to the reading age of 13, but this can easily be adjusted.
There are links to engaging YouTube videos.
Final activity is a PEE paragraph that includes peer-assessment examples on the next slide.

Norman Conquest reading pack
Multiple reading packs are included in this download. It can be used in the replacement of a textbook or for homework. This makes differentiation easy as the packs are broken down into different reading ages of 13, 10, and 8, but contain all the same information.
PDFs and Word versions are included so that the packs are easy to edit.
Topics included:
Anglo-Saxon England.
Contenders to the throne.
The Battle of Hastings.
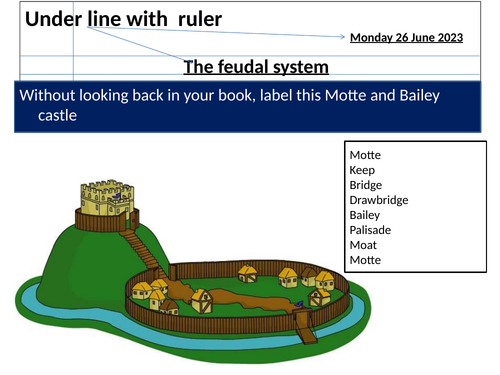
The Feudal system.
Motte and Bailey Castles.
Domesday Book.
Harrying of the North.
Significance of the Norman Conquest.

Henry VIII's Reformation (unit of work - KS3)
Six lessons, plus assessment.
- Lesson 1: What was the Reformation?
- Lesson 2: Henry VIII’s Great Matter
- Lesson 3: Break with Rome
- Lesson 4: Religious transformation of England.
- Lesson 5: Wealth and power
- Lesson 6: Why did Henry VIII divorce Rome (assessment planning lesson)
- Lesson 7: Assessment
Most lessons include reading and links to engaging videos on YouTube.
Reading Packs
Three different reading packs (reading ages of 13, 10, and 8).
Answers are included for each reading pack to allow quick self-assessment.
SoW
A written SoW is included. The SoW breaks down each lesson into three learning objectives with activities connected to each objective. All activities are included on each PowerPoint. This unit includes self assessment, peer-assessment and teacher assessment at the final lesson.
This is a plug-and-play lesson. No additional planning is needed. Just print the reading packs. Where there is reading in a lesson the 13-year reading age has been included in the PowerPoint. It is easy to swap this out for the self assessment part of the lesson

Norman Conquest (Unit of work): how did William take control of England?
Seven lessons including assessment lesson.
Each lesson includes reading and a clip from YouTube.
The reading is differentiated by reading age (Reading ages of 13, 10, and 8). You can swap out different reading packs, depending on ability. All packs are included.
Written SoW.
All lessons work towards the end question: how did William take control of England?
Bundle

Edexcel Cold War Lessons and resources
Bundle covers the entire Period Study.
Includes exam questions and mark schemes
Printable resources included
AfL includes answers on the next slide.

Edexcel Cold War Key Topic 3
This series of lessons follows Edexcel’s Superpower relations and the Cold War, 1941–91. There are printable information sheets, but this can be esily substituted with the textbook.
Seven lessons in total with resources to print.
Invasion of Afghanistan and Carter
Detente (2 lessons)
Second Cold War
Gorbachev’s new thinking (2 lessons)
Fall of the Berlin Wall
Collapse of the SU and end of Warsaw
KT3 over view lessons with worksheet
KT3 exam questions with mark schemes
Every lesson starts of with 5 recall questions with the answers
Exam questions with the mark scheme are included
Self assessment is included.
Mark schemes are included on the ppts to make peer assessment easy.
Each each question relevant to KT3 is included in the exam question ppt. It is clear what part of th spec each exam question is referring to.

Edexcel Cold War Key topic 2
This is a series of lessons that follows the Edexcel P4 Superpower relations and the Cold War, 1941–91.
You don’t need the text book with this series of lessons but it can easily be substituted in.
7 lessons included with printable resources.
The Rufugee problem in Berlin
The Berlin Wall
Cuba (Bay of Pigs)
The Cuban Missile Crisis
Prague Spring ( 2 lessons)
Key Topic 2 overview lesson with worksheet
All exam questions and mark schemes relevant for Key topic 2 in one ppt.
All exam questions for this Key Topic are included (SAMs to 2022). Mark schemes included.
AfL activities included with answers after.
Each lessons starts off with recall activity (answers on the next slide).
Self assessment is included in the lesson.
Very Little editing required.

Edexcel Cold War Key Topic 1
This is a series of 10 lessons (with a ppt with all the exam Qs for this section) that follows Edexcel History Superpower relations and the Cold War, 1941–91. Exam questions are included within the lessons and in a separate ppt for revision.
You don’t need to published textbook with this series of lessons, but it can easily be substituted in.
Lessons in total with resources to print:
introduction to Cold War
Tehran, Yalta and Potsdam
Impact of the atomic bomb, telegrams, and Soviet satellite stats
Truman Doctrine
Cominform, Comecon, and NATO
Berlin Crisis
Significance of arms race and Warsaw Pact
Hungarian uprising (causes and Khrushchev’s response)
International reaction to invasion
A ppt with all the exam Qs (up to 2022) with mark schemes for key topic one.
An overview lesson with worksheet to accompany
Every lesson starts of with 5 recall questions with the answers
Past exam questions and mark schemes are included in the lessons
Exam questions with the mark scheme are included
Each activity had an AfL activity, often with answers
Possible to use the published textbook or to use the resources provided.

Edexcel History Elizabeth A3 revision sheets
Early Elizabethan England A3 revision sheet.
Could be used for cover lessons or as revision.
You will need the published textbook to go along with this.

Edexcel History Cold War revision sheets
A3 individual revision pack. You will need the published textbooks.

Cambridge IGCSE History B: 5. How effectively did the United States contain the spread of Cimmunism?
Included:
5.1 Causes of Korean War 1950-53
5.2 Events of the Korean War
5.3 Cuban Crisis
5.4 Consequences of Cuban Missile Crisis
5.5 Vietnam
5.6 Involvement in Vietnam war
5.7 Events in the Vietnam war
5.8 Reasons for withdrawal
5.9 summary Vietnam
Plus a bank of exam questions relevant to the topic

Cambridge IGCSE History B: 4. Who was to blame for the Cold War?
Eight lesson and knowledge tests
End of WW2
Yalta
Potsdam
Soviet expansion
USA’s reaction to Soviet expansion
Berlin Blockade
NATO and Warsaw
Who was to blame for the Cold War?
Knowledge questions with answer. Could use this as for low-stake regular testing.
Key words with definitions for part 4.
PPTs that explain how to analyse an historical source (i did not create this, they are just very useful, so i popped them in)

Cambridge IGCSE History B: 3. Why had international peace collapsed by 1939?
I used GCSE Modern World History, Ben Walsh. But i have provided alternative resources, if you don’t have access to this textbook
Nine lessons:
Hitler’s aims in foreign policy
The Saar, 1935 and Rhineland, 1936
Involvement in the Spanish Civil War, 1937
Appeasement
Anschluss, 1938
Crises over Czechoslovakia, 1938
Nazi Soviet Pact, 1939
The Outbreak of WW2, 1939
Exam Writing lesson

Cambridge IGCSE History B: 2. to what extent was the League of Nations a success?
10 lessons to cover the second question on the specification.
Long homework included.
Exam questions with mark schemes included.
**I used GCSE Modern World History, second edition to use with these ppts. ** However, i have included some alternative resources.
2.1: Structure of the League of Nations.
2.2: Successes of the 1920s
2.3: Impact of the Great Depression
2.4a: Manchuria 1
2.4b: Manchuria 2
2.4c: Manchuria source lesson
2.4d: Abyssinian Crisis
2.4e: Abyssinian Crisis 2
2.4f: Abyssinian Crisis source
2.4g LoN doomed from the start